Cybersecurity and Healthcare Consumers: My Conversation with Dr. Kaveh Safavi, Accenture

Patients are morphing into consumers, but with eyes wide open: they know about data breaches, and they increasingly demand healthcare services delivered on their own terms. I met with Accenture’s Dr. Kaveh Safavi, Frances Dare, and Jenn Francis at HIMSS17 to discuss their latest research into these two topics. In this post, I’ll cover the growing challenge of cybersecurity and what Accenture learned about consumer data breaches. Tomorrow I’ll discuss Accenture’s latest findings on the expectations of the evolving health/care consumer. [Spoiler alert: personal health information data security is one of those expectations]. At HIMSS17, the issue of cybersecurity is
Healthcare and the Autonomous Car: Setting the Stage for HIMSS17

The autonomous car is a metaphor for healthcare: that’s how my first interview kicking off the HIMSS marathon began. The annual 2017 HIMSS conference isn’t your father’s or mother’s HIMSS of ten years ago, or even the HIMSS of 2010 — the year that financial incentives for EHR adoption began to stream from the HITECH Act of 2009, motivating thousands of healthcare providers to acquire and meaningfully use digital health records systems. Then, the HIMSS conference floor was abuzz with EHR frenzy. This week, over 43,000 people working at the intersection of healthcare and technology have converged in Orlando, Florida, for
Doctors See Benefits in Patient Engagement Via Health IT
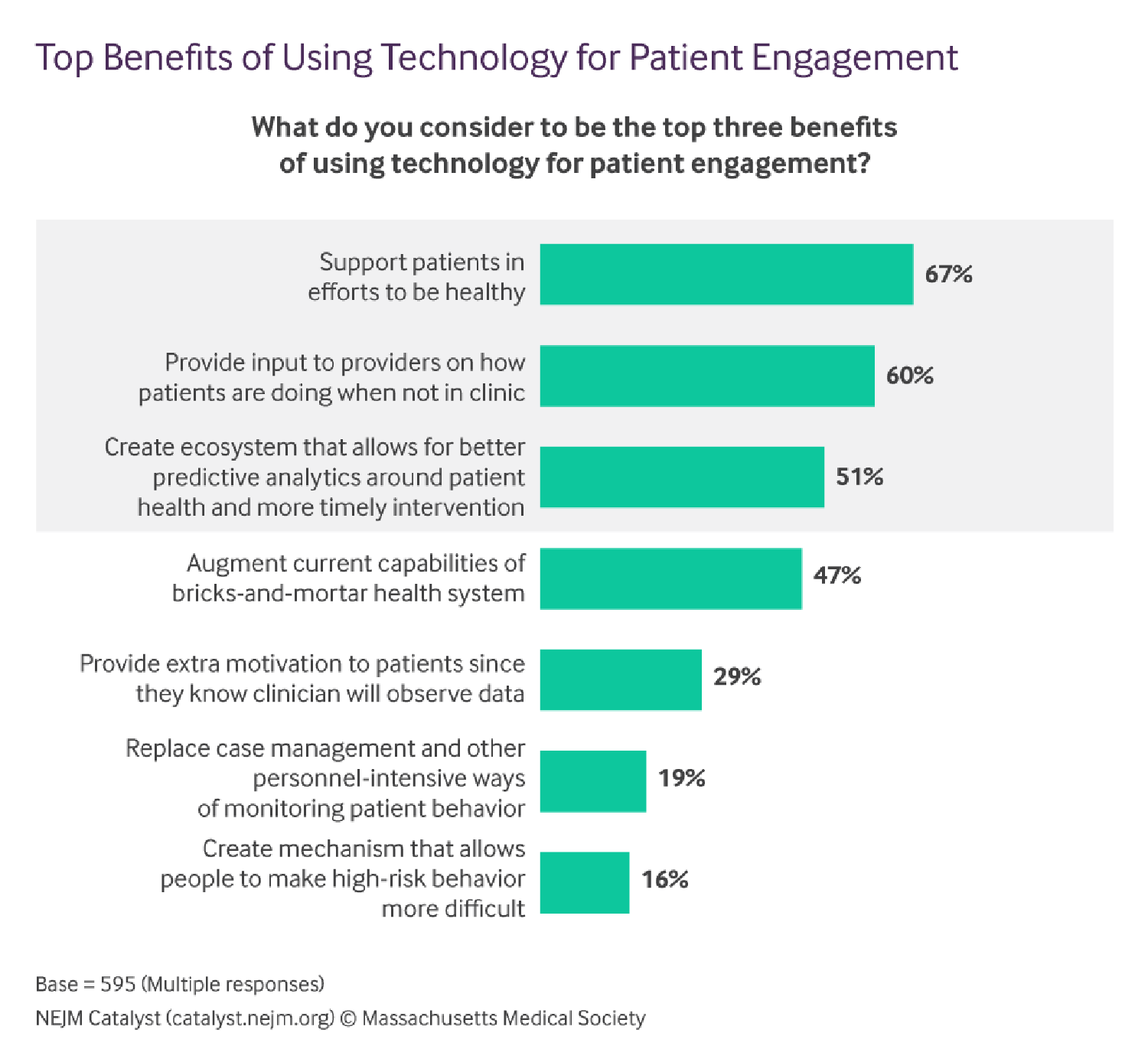
A special report on patient engagement and digital technology was published this month in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). Based on a survey of doctors and healthcare executives, the research found that clinicians and managers welcome the opportunity to use digital tech — when it makes financial sense. That conclusion inspired the title of the article, Patient Engagement Survey: Technology Tools Gain Support – But Cost Is a Hurdle. NEJM polled 595 members of the NEJM Catalyst Insights Council, which included healthcare executives and clinicians who deliver healthcare. Here is NEJM’s scenario on patient-engaging health IT, a Holy Grail of sorts:
Pharma’s Branding Problem – Profits Over Patients
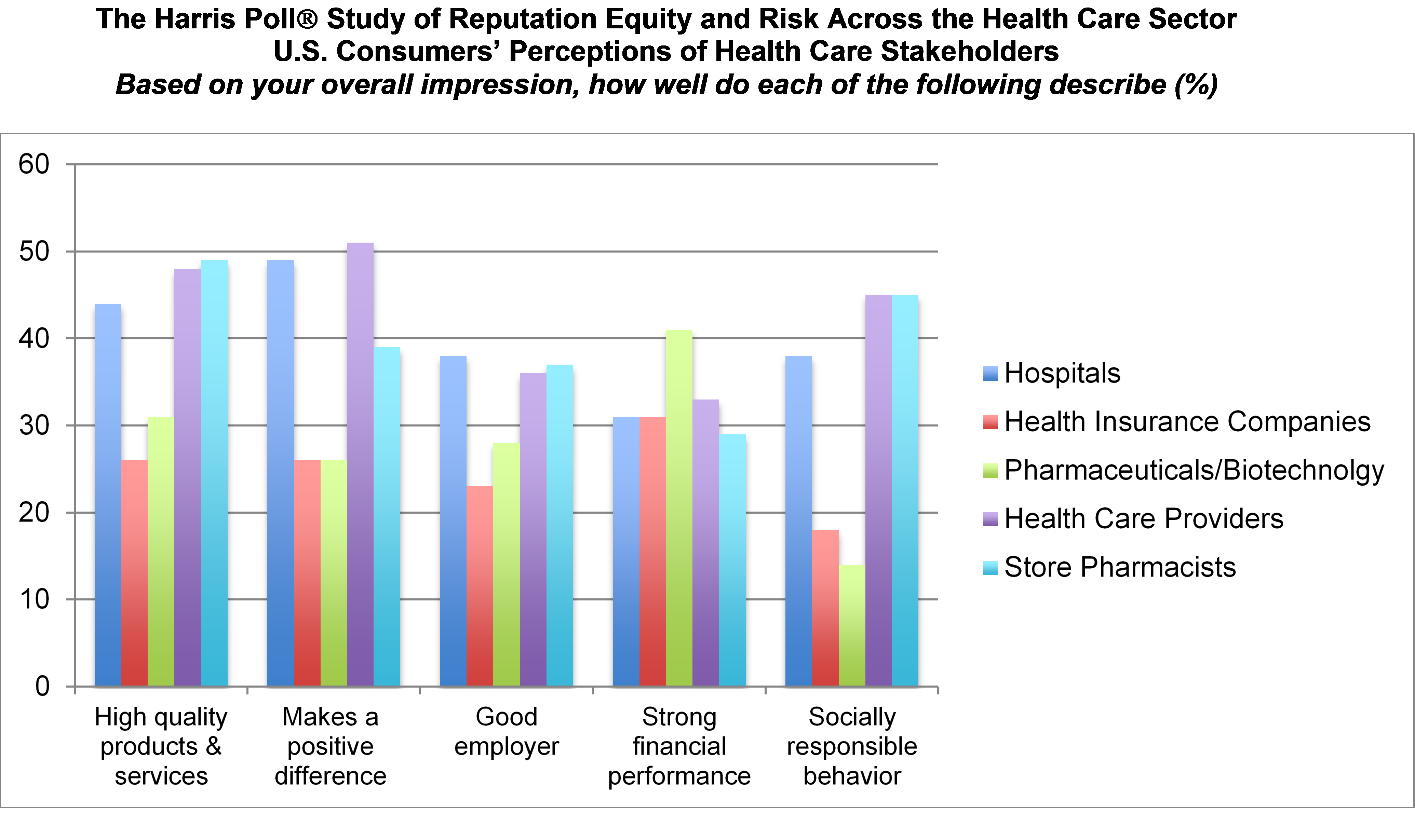
Nine in 10 U.S. consumers think pharma and biotech put profits above patient interests, according to the latest Harris Poll studying reputation equity across organizations serving health care. Notice the relatively low position of the green bars in the first chart (with the exception of the impression for “strong financial performance); these are the pharma/biotech consumer impressions. The health industry stakeholders consumers believe would more likely place them above making money are health care providers, like doctors and nurses, hospitals, and pharmacists. Health insurance companies fare somewhat better than pharma and biotech in this Poll, although rank low on social
The Growth of Digital Health @Retail

This post was written to support the upcoming meeting of the PCHA, the Personal Connected Health Alliance, to be held 11-14 December 2016 at the Gaylord Hotel in greater Washington, DC. You can follow the events and social content via Twitter using the hashtag #Connect2Health. Have you visited your local Big Box, discount or consumer electronics store lately? You’ll find expanding shelf space for digital health technologies aimed squarely at consumers. 2017 promises even more of them, aimed at helping people accomplish health tasks once performed in hospitals and by healthcare providers, or tasks not yet delivered in today’s healthcare
Most Doctors With EHRs Still Not Taking Advantage of Their Benefits
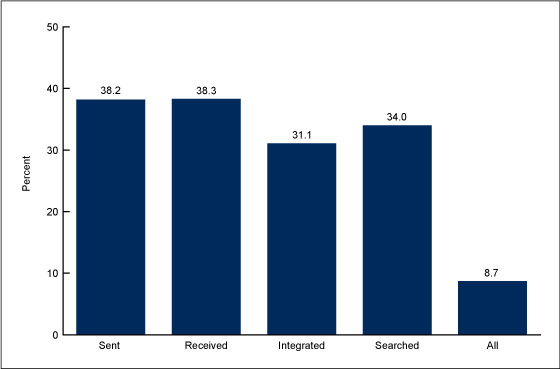
Interoperability of medical records across physician offices remained elusive in 2015, according to the latest data reported out by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). About 8 in 10 U.S. physicians had an electronic health records system in 2015. One-third of these doctors electronically sent, received, integrated or searched for patient health information — indicating that most physicians still aren’t using EHRs to their fullest extent. These findings come from the NCHS Data Brief from the CDC, State Variation in Electronic Sharing of Information in Physician Offices: United States, 2015. The bar chart illustrates the percentage of U.S. office-based doctors
Doctors Are Growing to Like Digital Health Tools, Says the AMA
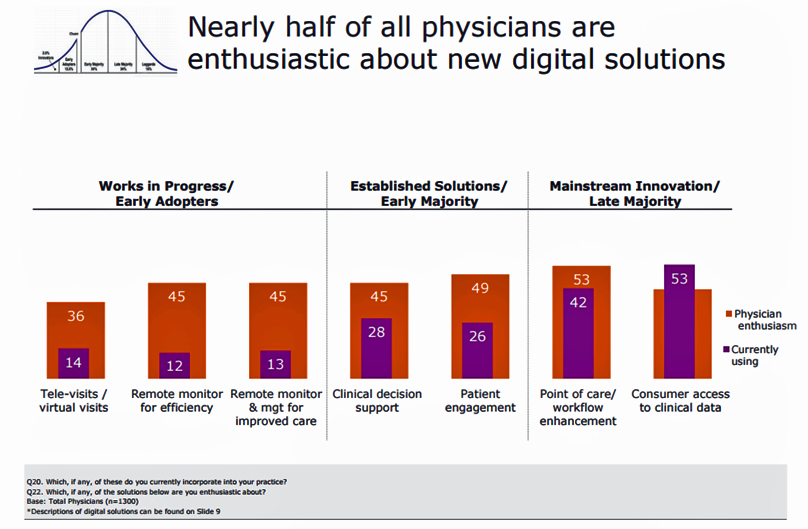
Notwithstanding the head of the AMA recently referring to digital health technologies as “snake oil,” it appears that one-half of physicians is keen on digital health. And scale, not age, matters when it comes to doctors using digital health tools. The American Medical Association (AMA) surveyed physicians on their use of digital health tools, finding that primary care physicians (PCPs) and doctors working in larger and more complex practices tend to be more digital. In Physicians’ motivations and requirements for adopting digital clinical tools, the AMA’s digital health study, “Physicians are optimistic about digital health innovation and its game-changing potential
Most Digital Health Consumers Say They Benefit from Connected Health
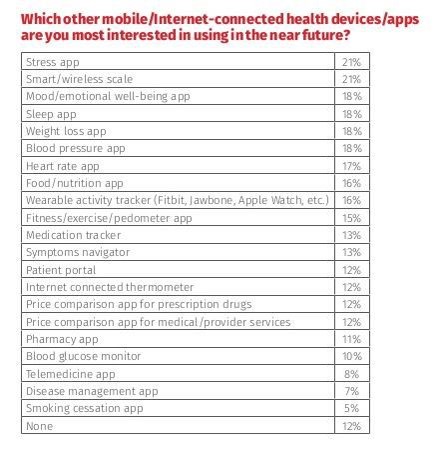
Managing stress, weight, mental health, sleep, and heart function are among the top-most desired reasons already-connected health consumers are interested in further connecting their health, according to The 2016 HealthMine Digital Health Report. The most popular tools people use to digitally manage their health deal with fitness and exercise (among 50% of connected health consumers), food and nutrition (for 46%), and weight loss (for 39%). 3 in 4 people who use digital health tools say they have improved their health by connecting to these tools. 57% of digital health users also say going health-digital has lowered their healthcare costs. The survey
Consumers Seek Quality and Privacy In Tech-Enabled Healthcare
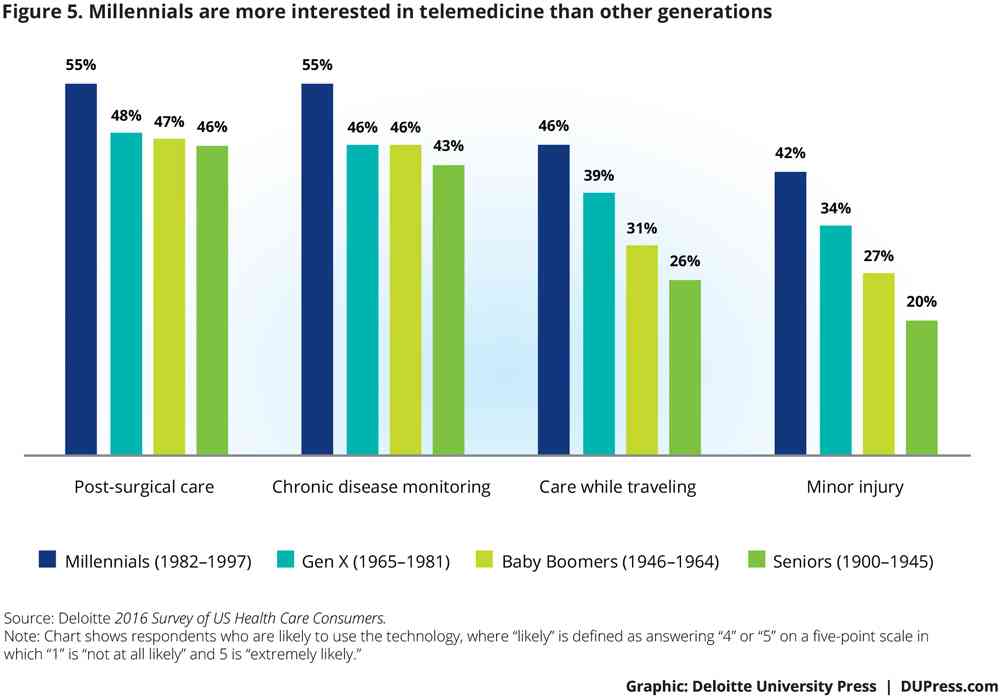
Consumers are open to technology-enabled healthcare, but look to providers to ensure quality and privacy of patients’ personal health information, according to Will Patients and Caregivers Embrace Tech-Enabled Healthcare?, based on the Deloitte 2016 Survey of US Health Care Consumers. Seven in 10 consumers would use at least one of the technologies Deloitte served up in its study, with telemedicine at the top of the list: 49% of people favor telemedicine for post-surgical care, 48% for chronic disease management, 36% for care while traveling, and 32% for minor health issues. While Millennials are generally keener across-the-board for tech-enabled health care,
Retail Clinics Continue to Shape Local Healthcare Markets
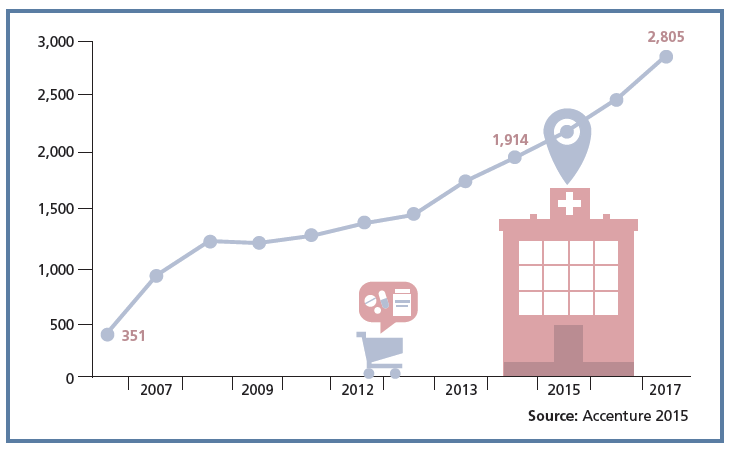
Retail clinics are a growing source of primary care for more U.S. health consumers, discussed in a review of retail clinics published by Drug Store News in July 2016. There will be more than 2,800 retail clinics by 2018, according to Accenture’s tea leaves. Two key drivers will bolster retail clinics’ relevance and quality in local health delivery systems: Retail clinics’ ability to forge relationships with legacy health care providers (physicians, hospitals); and, Clinics’ adoption and effective use of information technology that enables data sharing (e.g., to the healthcare provider’s electronic health records system) and data liquidity (that is, securely moving
U.S. Health Spending Will Comprise 20% of GDP in 2025
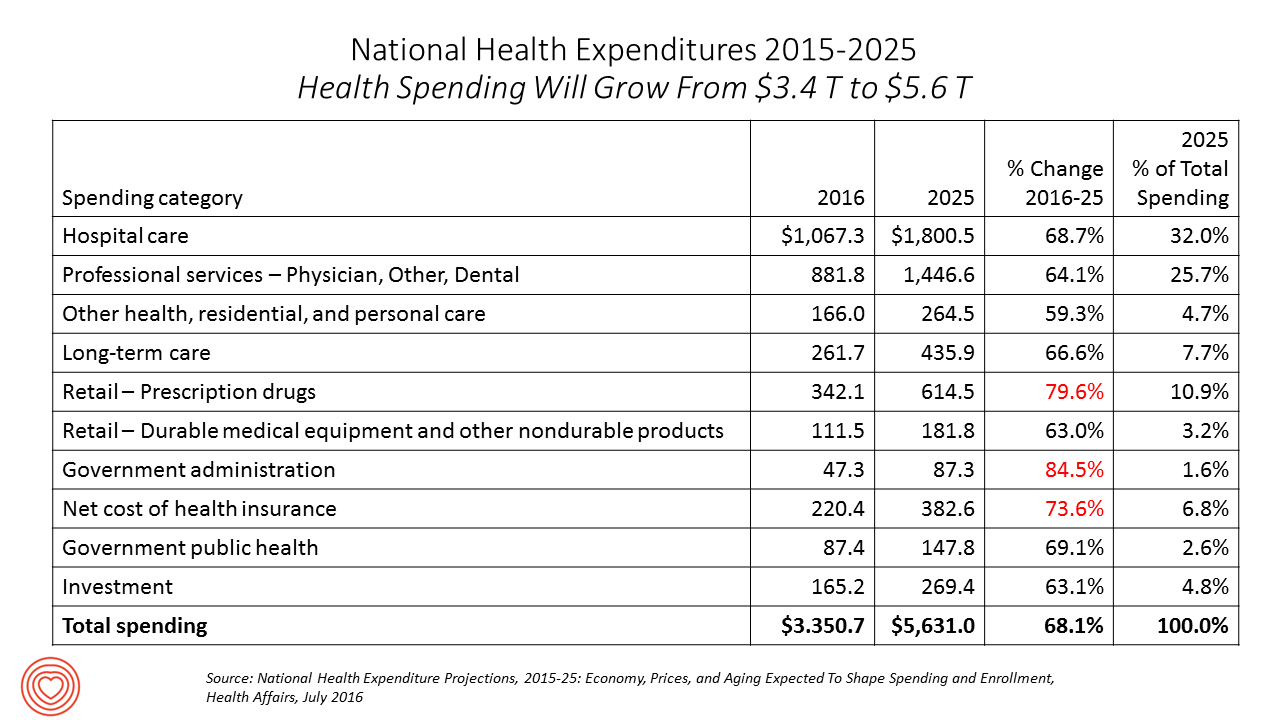
Spending on health care in America will comprise $1 in every $5 of gross domestic product in 2025, according to National Health Expenditure Projections, 2015-25: Economy, Prices, And Aging Expected to Shape Spending and Enrollment, featured in the Health Affairs July 2016 issue. Details on national health spending are shown by line item in the table, excerpted from the article. Health spending will grow by 5.8% per year, on average, between 2015 and 2025, based on the calculations by the actuarial team from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), authors of the study. The team noted that the Affordable Care
Salesforce on the State of the Connected Patient: Willing But Not There Yet
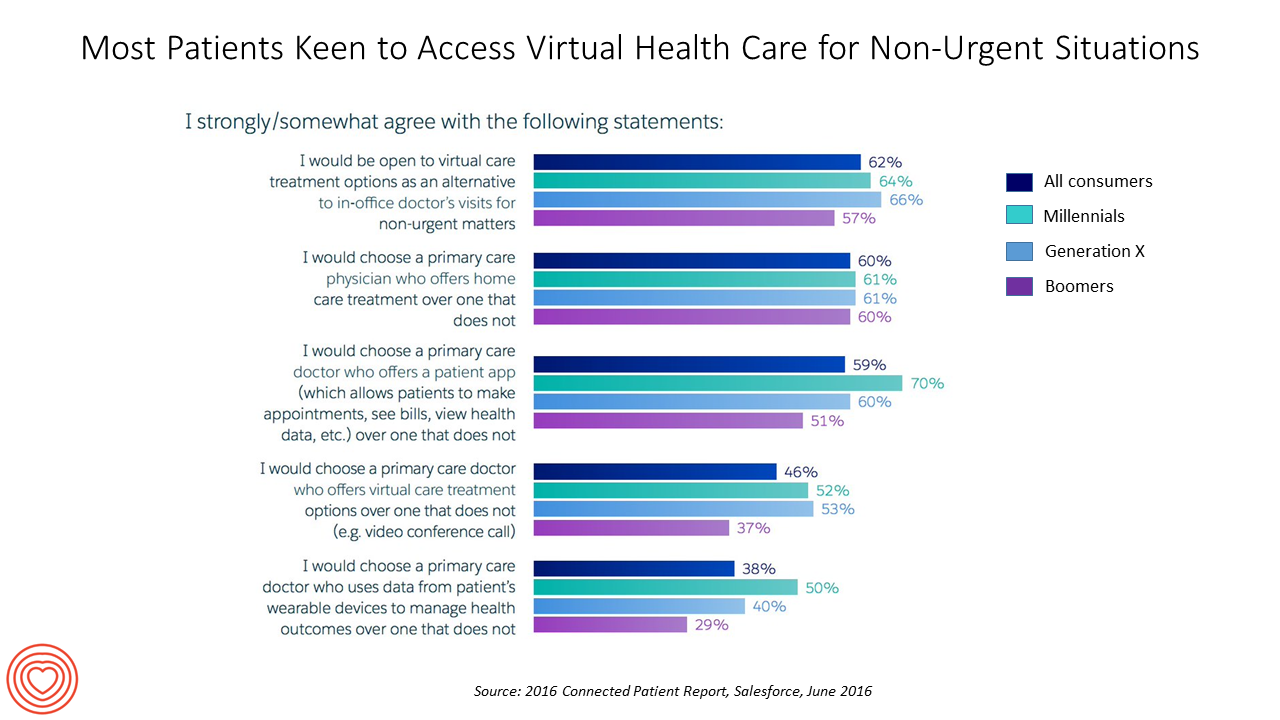
About two-thirds of health consumers would be open to virtual health care options for non-urgent situations, according to the 2016 Connected Patient Report from Salesforce Research. Salesforce conducted the survey with the Harris Poll online among 2,025 U.S. adults in June 2016. 1,736 of these health consumers had health insurance and a primary care physician. Among the many findings in the report, Salesforce found that: In terms of communications and relationship… The vast majority of consumers with primary care physicians are very satisfied with them (91% of people with PCPs) However, one-third of people with a PCP believe their physicians would
What Health Care Can Learn from the Blood Clot Community

“Our goal is to create an aware and engaged, irritating set of patients who create a dialogue with health care providers once they’ve had a [blood] clot,” explained Randy Fenninger, CEO of the National Blood Clot Alliance (NBCA). NBCA’s tagline and hashtag is “Stop the Clot.” Welcome to the multi-stakeholder community involved with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and, clinically speaking, Venous Thromboembolism (VTE). We’re talking blood clots, and the public health burden of this condition is big: it’s a leading cause of death and disability. One in 4 people in the world die of conditions caused by thrombosis. I had
Costs and Connection At the Core of Consumers’ Health-Value Equations
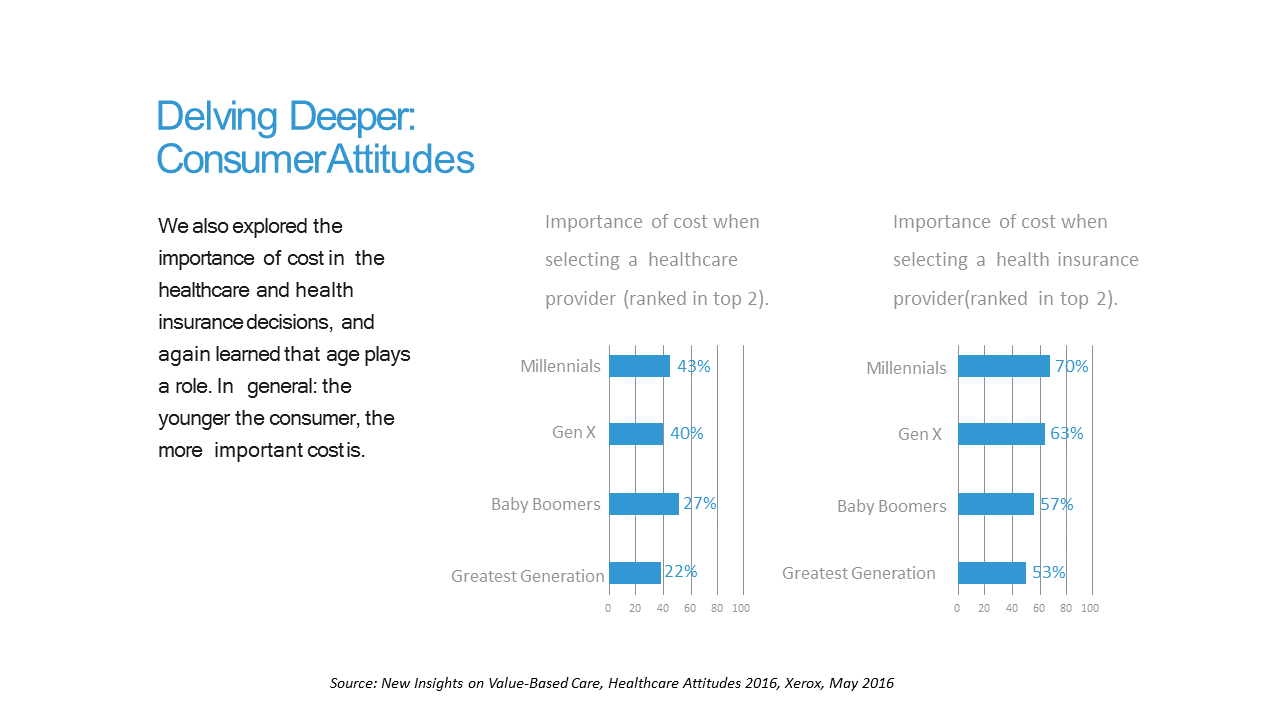
Cost ranks first among the factors of selecting health insurance for most Americans across the generations. As a result, most consumers are likely to shop around for both health providers and health plans, learned through a 2016 Xerox survey detailed in New Insights on Value-Based Care, Healthcare Attitudes 2016. The younger the consumer, the more important costs are, Xerox’s poll found, shown in the first chart. Thus, “shopping around” is more pronounced among younger health consumers — although a majority people who belong to Boomer and Greatest Generation cohorts do shop around for both health providers and health insurance plans —
Being A Doctor Is Highly Prestigious. A Politician? Don’t Ask.

The most prestigious occupation in America is being a doctor, agreed by 90% of U.S. adults. 90% of them would also encourage their child to pursue a career in medicine. Politician? 70% of parents would discourage a child from pursuing that career path, according to The Harris Poll’s survey on occupational prestige. The top-prestige professions are: Doctor, agreed by 90% Scientist, 83% Firefighter, 80% Military officer, 78% Engineer, 76% Nurse, 76% Architect, 72% Emergency medical tech, 72% Veterinarian, 71% Police office, 67%% Teacher, 65% Entrepreneur, 65% Chef, 62% Athlete, 62% Lawyer, 62% Musician, 61%. All other professions fell below 60%
People Want Healthcare Sherpas

8 in 10 Americans would like one trusted person to help them figure out their health care, according to the Accolade Consumer Healthcare Experience Index Poll, conducted by The Harris Poll. The study gauged how Americans feel about their healthcare, especially focusing on employer-sponsored health insurance. One-third of people (32%) aren’t comfortable with navigating medical benefits and the healthcare system; a roughly percentage of people aren’t comfortable with their personal knowledge to make financial investments, either (35%). Buying a car, a home, technology and electronics? Consumers are much more comfortable shopping for these things. Consumers say that the most onerous
The Patient-Physician Experience Gap
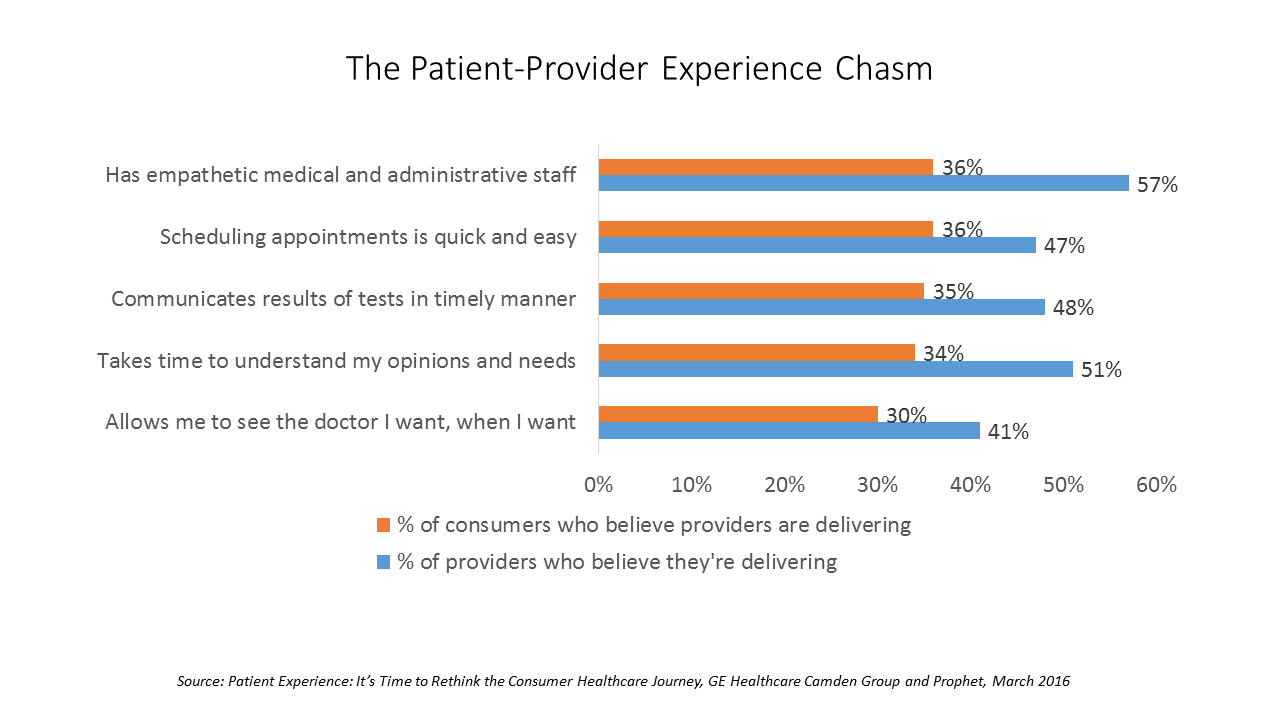
As patients continue to grow health consumer muscles, their ability to vote with their feet for health care services and products grows. That’s why it’s crucial for health care providers to understand how patients perceive their quality and service levels, explained in Patient Experience: It’s Time to Rethink the Consumer Healthcare Journey, a survey report from GE Healthcare Camden Group and Prophet, a brand and marketing consultancy. 3 in 4 frequent healthcare consumers say they are frustrated with their services. One-half of less-frequent patients are frustrated. Patients and physicians are on different pages when it comes to evaluating the health care
Yin and Yang: Doctors and Patients’ Bipolar Views on EHR Access
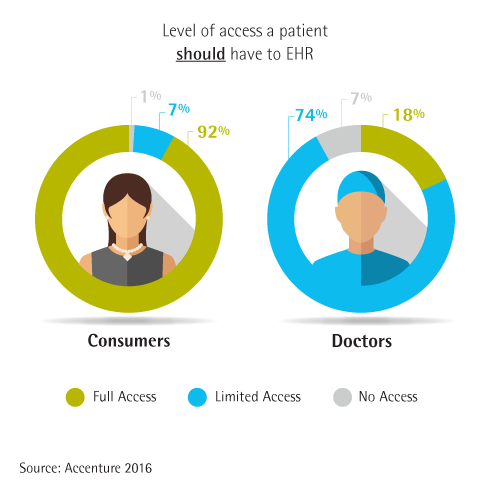
Patients are from Mars and Doctors from Venus when it comes to their views on whether consumers should have full access to their electronic health records (EHRs), according to a survey from Accenture released this week at the 2016 meeting of the HIMSS conference in Las Vegas. The vast majority of consumers are keen to access their full EHR, compared to a majority of doctors who advocate for limited access, as the circle diagram dramatically illustrates. The “old days” of patient information asymmetry — with a paper-based folder that got locked up in a health records cabinet — are gone.
Health Consumers Happy With Doctor Visits, But Want More Technology Options
9 in 10 adults in the U.S. have visited a doctor’s office in the past year, and over half of these patients have been very satisfied with the visit; 35% have been “somewhat” satisfied. Being a highly-satisfied patient depends on how old you are: if you’re 70 or older, two-thirds of people are the most satisfied. Millennial or Gen X? Less than half. What underlies patient satisfaction across generations is the fact that younger people tend to compare their health care experience to other retail experiences, like visiting a bank, staying at a hotel, or shopping in a department store.
The Health Information Economy – Better With Patients
“Consumers expect to have their data available and shareable.” Two essays in two issues in the past two weeks of The New England Journal of Medicine point to the importance of patients – people, caregivers, consumers, all — in the morphing “health information economy,” a phrase used in the title of one of the published pieces. In Time for a Patient-Driven Health Information Economy, Dr. Ken Mandl and Dr. Isaac Kohane, who are both affiliated with the Department of Biomedical Informatics at Harvard, discuss peoples’ growing interest in engaging with their personal health information, noting frustrating barriers to doing so:
Looking for Health at CES 2016
The Internet of Healthy and Medical Things will proliferate at CES 2016 in Las Vegas next week – the annual Consumer Electronics Show. This is the yearly mega-convention organized by the Consumer Technology Association, and digital health has been among the fastest-growing marketplaces at the CES for several years in a row. The two-day Digital Health Summit will complement the vendors ont he convention floor with content, education, and networking for the industry. Here’s a link to my latest Huffington Post column on Health at the 2016 Consumer Electronics Show – What to Expect. Health Populi’s Hot Points: The Consumer
Yes, Virginia, There Really Are Healthcare Consumers: McKinsey
“There’s no such thing as a healthcare consumer. No one really wants to consume healthcare,” naysayers tell me, critical of my all health-consmer-all-the-time bully pulpit. But, touché to my health consumer-critics! I’ve more evidence refuting the healthcare consumer detractors from McKinsey in their research report, Debunking common myths about healthcare consumerism, from the team working in McKinsey’s Healthcare Systems and Services Practice. Their survey research among over 11,000 U.S. adults uncovered 8 myths about the emerging American health consumer, including: Healthcare is different from other industries Consumers know what they want from healthcare and what drives their decisions Most consumers
Growing Signs Of Consumer Health Engagement, Via Deloitte
A growing desire for shared decision making with doctors. Increasing trust and consumption of health care information online, in social media, and report cards. Reliance on technology for monitoring health adn wellness, and medical conditions. Together, these three signals converge, illustrating a growing sense of consumer engagement among U.S. patients, found in the 2015 Deloitte Center for Health Solutions Survey of US Health Care Consumers. In Deloitte’s research summary, the title states that “No ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach” will work, given diversity among American health consumers. The sickest health consumers, Deloitte notes, have higher levels of health engagement and index higher on
Insurance Should Pay For End-of-Life Conversation, Most Patients Say
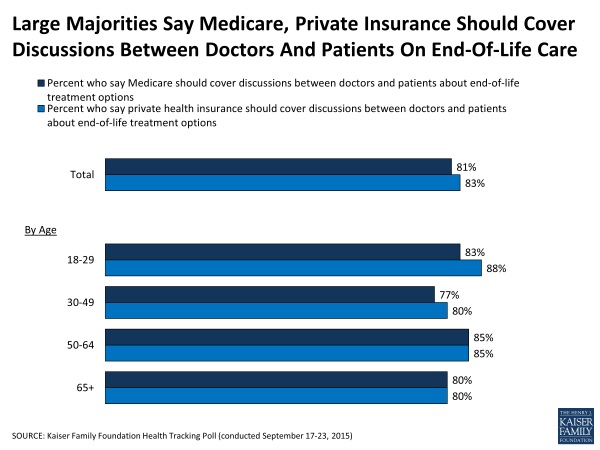
8 in 10 people in the U.S. say that Medicare as well as private health insurance plans should pay for discussions held between patients and doctors about hatlhcare at the end-of-life. The September 2015 Kaiser Family Foundation Health Tracking Poll asks people their opinions about talking end-of-life with their doctors. The vast majority of people support the concept and physicians being paid for holding such conversations in doctor-patient relationship. The question is germane because the Obama Administration has announced plans to pay doctors for office visits to discuss end-of-life (EOL) issues with Medicare patients. There isn’t a huge variation across
IoT in Healthcare, Take 2: Goldman Sachs weighs in
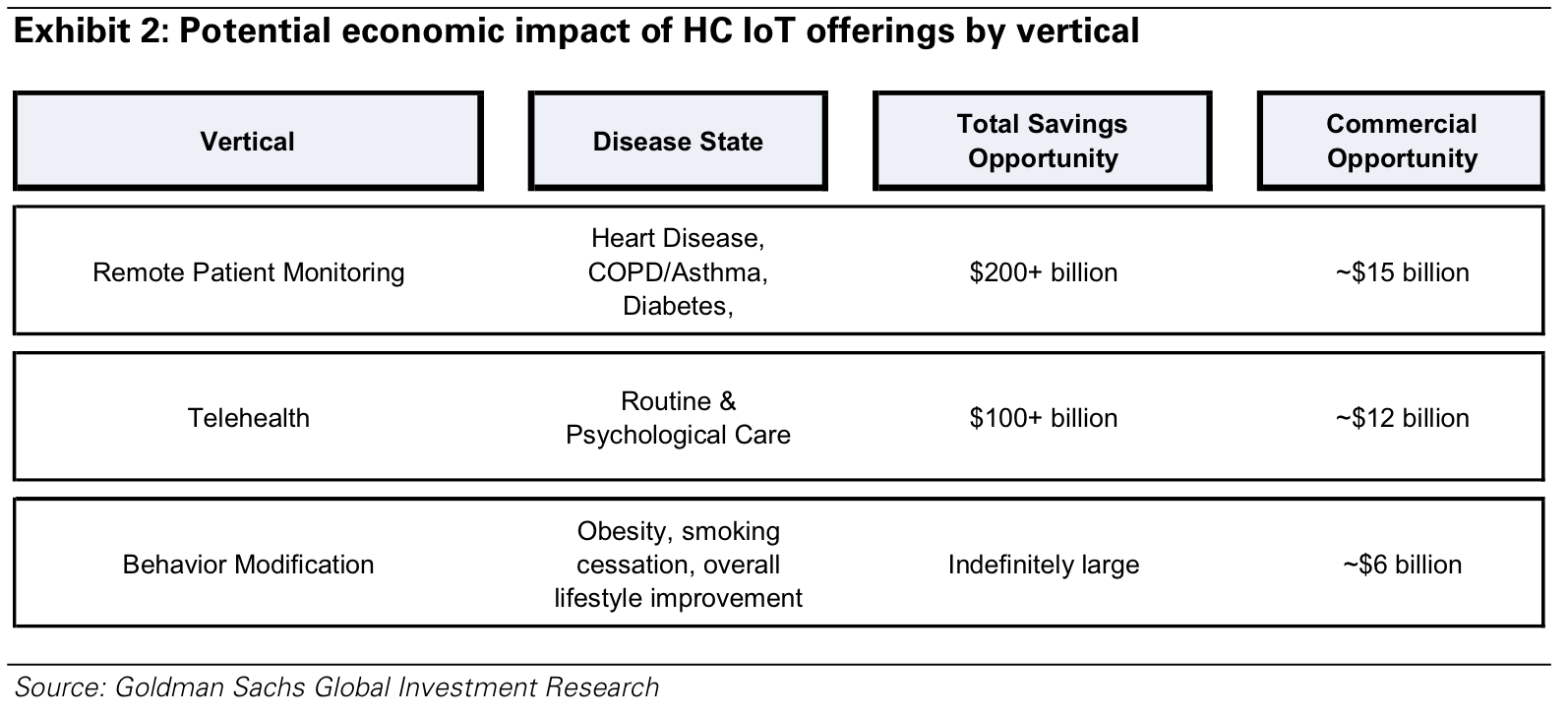
In this week’s posts on Health Populi, we’re diving into three big reports focused on digital health and the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare: from the McKinsey Global Institute, Goldman Sachs, and Accenture. In this post, we dig into Goldman Sachs’ analysis, The Digital Revolution comes to US Healthcare, the investment firm’s fifth volume in their Internet of Things report series. Goldman Sachs’ definition of the Healthcare IoT is, “a device that is connected via the Internet and informs clinical decision making,” which bridges digital and physical worlds “to change physician and patient behavior.” The firm identifies three IoT
All women are health workers
The spiritual and emotional top the physical in women’s definition of “health,” based on a multi-country survey conducted in Brazil, Germany, Japan, the UK and the U.S. The Power of the Purse, a research project sponsored by the Center for Talent Innovation, underscores women’s primary role as Chief Medical Officers in their families and social networks. The research was sponsored by health industry leaders including Aetna, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cardinal Health, Eli Lilly and Company, Johnson & Johnson, Merck & Co., Merck KGaA, MetLife, Pfizer, PwC, Strategy&, Teva, and WPP. The study’s summary infographic is titled How the Healthcare Industry Fails
#OwnYourHealth: Health is everywhere, even underground
Living my mantra of Health is Everywhere, where we live, work, play, pray, and shop, I am always on the lookout for signs of health in my daily life. Today I’m in Washington, DC, speaking on a webinar led by the National Council on Patient Information and Education (NCPIE), discussing the findings in a survey of U.S. adults on self-care health care – my shorthand for healthcareDIY. And the hashtag for the webinar also speaks volumes: #OwnYourHealth. Here’s the link to the survey resources. On my walk from Farragut North Metro station to a nearby office where the meeting will take place,
It’s a retail health world: consumers at the helm of health/care
Retail health v1.0 encompassed the pharmacy, then embraced urgent care and retail health clinics co-located in brick-and-mortar pharmacy chain stores. In v2.0, retail health encompasses all health/care, really, because people, patients and consumers are essentially self-insured up to the point when their health plan kicks in some cash. The high-deductible health plan era is ushering in the retail health era, broadly writ. Hospitals & Health Networks magazine (HHN) ran a story titled Think Like a Retailer to Engage Patients, covering founder of WEGO Health Jack Barrette‘s and my panel presentation at the 2015 HIMSS conference in Chicago last week. Writer
Doctors who write right: Gawande, Topol and Wachter put people at the center of health/care
There’s a trifecta of books written by three brilliant doctors that, together, provide a roadmap for the 21st century continuum of health care: The Patient Will See You Now by Eric Topol, MD; The Digital Doctor from Robert Wachter, MD; and, Being Mortal, by Atul Gawande. Each book’s take provides a lens, through the eyes of a hands-on healthcare provider, on healthcare delivery today (the good, the warts and all) and solutions based on their unique points-of-view. This triple-review will move, purposefully, from the digitally, technology optimistic “Gutenberg moment” for democratizing medicine per Dr. Topol, to the end-game importance of
Hug your physician – chances are, s/he’s burned out
If you’re meeting with a physician in the next week or two, put on your empathy hat: chances are, they are feeling burned-out. Overall 46% of physicians report they were burned out in 2014, up from just under 40% last year. Medscape’s Physician Lifestyle Report 2015 finds that at least one-half of physicians are burned-out who work in critical care, emergency medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, general surgery, and infectious disease (including HIV). And, at least 37% of physicians are burned-out working in all other specialties, shown in the first chart. Medscape gauges doctors’ self-assessments of burnout with a lens
Patients and providers on health care: whose cost is it, anyway?
The one aspect of American health care that unites consumers and providers alike is cost, which is driving high anxiety among both providers and patients. Most of them also agree that the American health care system is on the wrong track. For patients, the anxiety is about ability to pay for and access the health care service to which they’ve become accustomed. For providers (and especially those over 55 years of age), the anxiety about costs is doctors’ and hospitals’ ability to survive in the uncertain health-economic environment. The survey report, How We View Health Care in America, marks the first
People don’t know much about patient portals: Xerox’s 5th EHR study
The Field of Dreams works in nostalgic plotlines about baseball, but as I’ve pointed out since the advent of consumer-facing health technologies, there’s no Field of Dreams effect in health care when it comes to consumer health engagement. U.S. health consumers aren’t using the patient portals that health care providers have built as part of their efforts to bolster health engagement via EHRs and health IT, Xerox found in the company’s 5th annual survey on electronic health records. I spoke with Tamara St. Claire to discuss the implications of the consumer poll, which was conducted among 2,017 U.S. adults in
Digital and mobile health: can doctors and consumers get on the same wavelength?
There’s growing interest among both consumers and clinicians in people DIY’ing healthcare. Consumers are even keener than their doctors about the self-care concept, PwC’s Health Research Institute has found. Doctors who are already in value-based payment mode — participating in accountable care organizations, at-risk for reimbursement, doing population health — are earlier adopters of digital health tools that enable patients to care for themselves outside of the health care setting. These providers are also working more on care teams, where physicians can work at their ‘highest and best use,’ complemented by nurse practitioners, physician assistants, diabetes educators, and other ancillary
Live from the 11th annual Connected Health Symposium – Keeping Telehealth Real
Dr. Joseph Kvedar has led the Center for Connected Health for as long as I’ve used the word “telehealth” in my work – over 20 years. After two decades, the Center and other pioneers in connected health have evidence proving the benefits, ROI (“hard” in terms of dollars, and “soft” in terms of patient and physician satisfaction), and technology efficacy for connecting health. The 11th Annual Connected Health Symposium is taking place as I write this post at the Seaport Hotel in Boston, bringing health providers, payers, plans and researchers together to share best practices, learnings and evidence supporting the
Hug your doctor: s/he needs it, according to the 2014 Physician Foundation survey
While the medical profession has reached a so-called state of crisis, there’s also a “changing of the guard” happening in the profession where doctors are re-imagining what it means to be physician in the era of value-based, technology-enabled health care. Such is the state of the union — or dis-union — of the U.S. medical profession. The 2014 Survey of America’s Physicians from Physicians Foundation finds that 4 in 5 U.S. doctors are over-extended or reaching full capacity in their practices. This is up from 2012. Only 19% of doctors say they have time to see more patients. That may be
Crossing the digital health chasm between consumers and providers – talking with Dr. Eric Topol
More than twice as many patients than physicians are embracing consumers’ use of new digital technologies to self-diagnose medical conditions on their own. On the other hand, 91% of doctors are concerned about giving patients access to their detailed electronic health records, anticipating patients will feel anxious about the results; only 34% of consumers are concerned about anxiety-due-to-EHR-exposure. Welcome to the digital health chasm, that gap between what consumers want out of digital health, and what doctors believe patients can handle at this stage in EHR adoption in doctors’ offices and in patients’ lives. I have the video of Jack
Dr Eric Topol on the digital democratization of health care
Moore’s Law is coming to medicine. And it will look and feel a lot like Uber: with rich technology underpinning, consumer-service oriented and friendly, and shaking up the professionals at the front line of the business (from taxi drivers to physicians). Eric Topol, physician and editor-in-chief at Medscape, told a standing-room-only audience at the kickoff of the 8th annual Health 2.0 Conference that the democratization of health care is coming based on consumers’ use of eight drivers: sensors, labs, imaging, physical exams, access to medical records, transparency of costs, and digital pills. Dr. Topol referred to the cover ot TIME
Health economics in the exam room: doctors and patients discussing the costs of health care
A new conversation has begun between doctors and patients: talking about money and health care, and what treatments cost — specifically, what a particular treatment will cost a patient, out-of-pocket. Over a dozen physician professional societies are proponents of these discussions, and are providing support to doctors in their networks. Doctors already engaging in the topic of the cost of care with patients aren’t being altruistic about spending this precious time in the already-time-constrained patient encounter: these discussions are increasingly relevant to physicians’ financial outcomes. I’ll be addressing this new feature in the doctor’s office at the upcoming Point-of-Care conference,
Do EHRs “chill” patient disclosures to clinicians?
Patients are concerned about private risks of personal health data, resulting in some patients not disclosing certain information to health providers to protect their perceived EHR privacy and security risks. Peoples’ mixed feelings about sharing personal health information with their providers and EHRs is explored in The double-edged sword of electronic health records: implications for patient disclosure, published in the July 2014 issue of JAMIA, the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA). “The perception of the [EHR] technology may elicit non-disclosure as a privacy-protecting behavior,” the authors warn. Celeste Campos-Castillo and Denise Anthony, the paper’s researchers who work in
Dialing Dr. Verizon – the telecomms company launches virtual house calls
Expanding its wireless footprint in health care, Verizon, the telecommunications company, announced the start of Verizon Virtual Visits today. The program will be marketed to employers and health plans to enable patients to see doctors at home or when traveling, via Verizon’s wireless network. I spoke with Christine Izui, Verizon’s quality officer, mobile health solution, earlier this week about Virtual Visits. We discussed the market forces that support the growth of telehealth and, in particular, physician visits “anywhere:” There is an under-supply and poor distribution of primary care doctors and certain specialties around the U.S. Employers and health plan sponsors are
Practice Fusion joins the open health data community with Insight
Open data is a growing trend in health care. Analyzing data sets across lots and lots of people can help researchers identify medical cures, anticipate epidemics, and solve knotty problems where social and behavioral issues complicate clinical questions and solutions. Joining the open health data community is the health IT company Practice Fusion, which is sharing with the public aggregated data on some 81 million patients collected through over 100,000 active users every month recording patient data in the company’s cloud-based electronic health records system. Insight, the searchable database, is freely available to people, researchers, policymakers, and anyone who wants to look at top line
The Season of Healthcare Transparency – Consumer Payments and Tools, Part 4
“The surge in HDHP enrollment is causing patients to become consumers of healthcare,” begins a report documenting the rise of patients making more payments to health providers. Patients’ payments to providers have increased 72% since 2011. And, 78% of providers mail paper statements to patients to collect what they’re owed. “HDHPs” are high-deductible health plans, the growing thing in health insurance for consumers now faced with paying for health care first out-of-pocket before their health plan coverage kicks in. And those health consumers’ expectations for convenience in payment methods is causing dissatisfaction, negatively affecting these individuals and their health providers’
Doctors become health economists
The rising costs of health care in America, and consumers’ growing cost burdens, has many impacts on the U.S. health ecosystem. In particular, patients have been self-rationing due to costs, without necessarily paying attention to quality or medical outcomes. Doctors have begun to pay more attention to costs and their impacts on patients in their practices, addressed in today’s New York Times article, Treatment costs could influence doctors’ advice to patients. Andrew Pollack writes in the Times about the morphing role of doctors, some of whom are taking on the mantle of being a “steward of society,” as characterized by
The digital health bubble – is it about to burst? #SXSW
That’s a useful and timely question, given the news that Castlight Health will launch its IPO with valuations north of $1 billion. Yes, “billions,” and according to a MarketWatch analysis, “it’s a bargain at $1 billion.” So then – do we anticipate a bubble? asked Marc Monseau of the Mint Collective, the convener of our panel who brought together Robert Stern, a successful health-tech entrepreneur whose latest venture, @PointofCare, focuses on patient engagement; Marco Smit of Next Innovation Health Partners (parting from the Health 2.0 Conference family where he led Health 2.0 Advisors for several years); and me. Some key
Risk-shift: employers continue to push more risk to employees and families for health costs
With health costs increase increasing at 4.4% in 2014, a slightly higher rate of growth than the 4.1% seen in 2013. While this is lower than the double-digit increases U.S. employers faced in 2001-2004, it’s still twice the rate of general consumer price inflation. That’s what the first graph shows, based on the The 19th Annual Towers Watson/National Business Group on Health Employer Survey on Purchasing Value in Health Care. Employers generally want to continue to provide health insurance…for the time being. 92% of companies expect to make changes in health plan provisions in 2014, with 1 in 2 anticipating “significant
Patient engagement and mobile health – design and timing matter
Thinking about personal health information technology – the wearable devices, remote health monitors, digital weight scales, and Bluetooth-enabled medical equipment scaled for the home – there are two glasses. One is half-full and the other, half-empty. The half-full glass is the proliferation of consumer-facing devices like Fitbit, Jawbone and Nike, which comprise the lion’s market share in the health wearables segment; the mass adoption of mobile phones and tablets; consumers’ multi-screen media behavior (as tracked by Nielsen); and consumers’ growing share of medical spending, now about 40% of annual spending (or something north of $8,000 for a family of four
Doctor respect, nurse trust – the yin/yang of team-based care
7 in 10 people in the U.S. see a doctor for their health care, and prefer seeing a doctor over a nurse practitioner, based on a poll Ipsos conducted on behalf of the American Academy of Family Physicians. What do people seek in a doctor? Knowledge, state-of-the-art treatments, experience and trustworthiness are the top traits people seek in health providers overall. Ipsos probed further into various traits for clinicians (including doctors, nurses and NPs), asking which of these factors were embodied in the health professional people want to receive care from. The most important attributes for doctors were: Who I want
Nurses are the most-trusted professionals in America
Who do you trust? If you’re a member of the middle of the U.S. normal bell curve, you’re thinking “nurses.” 8 in 10 Americans put nurses at the top of the ethics list, a question that Gallup has frequently surveyed since 1976. Nurses have ranked highest in honesty and ethics in America since Gallup began included the profession in the poll in 1999 (except for 2001, when firefighters were #1 post 9/11). Tied for second place this year are pharmacists and grade school teachers (with 70% of U.S. adults ranking them with high ethical standards), closely followed by doctors and
Don’t over-forecast mobile health in the short-run
The 2013 Mobile Health Summit was hosted by HIMSS at The Gaylord Resort in suburban Washington DC, taking place over 4 days during the mid-atlantic region’s iciest conditions in years. But inside the cocoon of this convention space, 5,000 conveners took in demonstrations of innovations using mobile platforms and standards that extend health services, knowledge and self-help tools to people and providers. Several themes emerged out of the meeting… Lots of apps, too few business models. There are too many apps and not enough companies, Esther Dyson noted in a keynote session during which she dialogued with two Steve’s: Steven
Make health care “feel” more like retail via transparency
Consumers who are well-covered by health insurance are in favor of talking about costs with their doctors. This research finding illustrates the fact that price transparency in health care isn’t just the concern of un- and under-insured people, but that shining the light on the price of health care is everybody’s business. But it’s also the case that most physicians aren’t yet involved in these health-financial conversations with their patients. Two studies presented at the recent 2013 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) learned that patients are keen to know more about health care costs from
Moneytalk: why doctors and patients should talk about health finances
Money and health are two things most people don’t like to talk about. But if people and their doctors spoke more about health and finance, outcomes (both fiscal and physical) could improve. In late October 2013, Best Practices for Communicating with Patients on Financial Matters were published by the Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA). Michael Leavitt, former head of the Department of Health and Human Services, led the year-long development effort on behalf of HFMA, with input from patient advocates, the American Hospital Association, America’s Health Insurance Plans, the American Academy of Family Physicians and the National Patient Advocate Foundation, along
Innovating and thriving in value-based health – collaboration required
In health care, when money is tight, labor inputs like nurses and doctors stretched, and patients wanting to be treated like beloved Amazon consumers, what do you do? Why, innovate and thrive. This audacious Holy Grail was the topic for a panel II moderated today at the Connected Health Symposium, sponsored by Partners Heathcare, the Boston health system that includes Harvard’s hospitals and other blue chip health providers around the region. My panelists were 3 health ecosystem players who were not your typical discussants at this sort of meeting: none wore bow ties, and all were very entrepreneurial: Jeremy Delinsky
Consumers trust and welcome health and insurance providers to go DTC with communications
Consumers embrace ongoing dialog with the companies they do business with, Varolii Corporation toplines in a survey report, What Do Customers Want? A Growing Appetite for Customer Communications. Across all vertical industries consumers trust for this dialogue, health care organizations – specifically doctors, pharmacists, and insurance companies – are the most trusted. Examples of “welcome-comms” would be reminders about upcoming appointments or vaccinations (among 69% of people), notices to reorder or pick up a prescription (57%), and messages encouraging scheduling an appointment (39%). In banking, notices about fraudulent activity on one’s account is the most welcomed message beating out appointment
The new era of consumer health risk management: employers “migrate” risk
The current role of health insurance at work is that it’s the “benefits” part of “compensation and benefits.” Soon, benefits will simply be integrated into “compensation and compensation.” That is, employers will be transferring risk to employees for health care. This will translate into growing defined contribution and cost-shifting to employees. Health care sponsorship by employers is changing quite quickly, according to the 2013 Aon Hewitt Health Care Survey published in October 2013. Aon found that companies are shifting to individualized consumer-focused approaches that emphasize wellness and “health ownership” by workers to bolster behavior change and, ultimately, outcomes. The most
Taking vitamins can save money and impact the U.S. economy – and personal health
When certain people use certain dietary supplements, they can save money, according to a report from the Council for Responsible Nutrition and Frost and Sullivan, the analysts. The report is aptly titled, Smart Prevention – Health Care Cost Savings Resulting from the Targeted Use of Dietary Supplements. Its subtitle emphasizes the role of dietary supplements as a way to “combat unsustainable health care cost growth in the United States.” Specifically, the use of eight supplements in targeted individuals who can most benefit from them can save individuals and health systems billions of dollars. The eight money-saving supplements are: > Omega-3 > B
Consumers’ out-of-pocket health costs rising faster than wages – and a surprising hit from generic drug prices
U.S. health consumers faced greater out-of-pocket health care costs in 2012, especially for outpatient services (think: doctors’ visits) and generic drugs, as presented in The 2012 Health Care Cost and Utilization Report from the Health Care Cost Institute (HCCI) published in September 2013. At the same time between 2011 and 2012, wages grew about 3%, remaining fairly flat over the past decade as health care costs continued to grow much faster. HCCI found that per capita (per person) out-of-pocket growth for outpatient visits amounted to an average of $118 between 2011 and 2012. But the biggest share of out-of-pocket costs for
The FDA Has Spoken, and It Will Regulate “Some” mHealth Apps
The FDA has spoken: there are 2 statutory definitions for a mobile health tool as a “medical device” that the Agency says it has regulatory oversight: To be used as an accessory to a regulated medical device, or To transform a mobile platform into a regulated medical device. On page 8 of the Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff, you can read the FDA’s expanded definition of a mobile health app as being: “…intended for use in performing a medical device function (i.e. for diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or the cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention
Healing the Patient-Doctor Relationship with Health IT
A cadre of pioneering Americans has been meaningfully using personal health information technology (PHIT), largely outside of the U.S. health care system. These applications include self-tracking and wearable health technologies, mobile health apps, and digital medical tracking devices like glucometers that streamline tracking and recording blood glucose levels. In the meantime, only 21% of doctors surveyed by Accenture currently allow patients to have online access to their medical summary or patient chart – very basic components of the electronic health record. We know what’s primarily driving health providers’ adoption of health IT: namely, the HITECH Act’s provisions for incentives. But
Health information search online, an hour a week. Time with a doctor? An hour a year.
In game-scoring unit terms, 52 is the number of hours an average American spends seeking health information online each year. The 1 (hour) is roughly equivalent to the approximate total time a patient spends with a physician (an average of 3 visits, with an average time per vision of 20 minutes). Thus, 52:1. This means that the average U.S. health consumer spends much more time DIYing her health using digital information resources than speaking face-to-face with their physician in the doctor’s office. Still, the physician continues to be a go-to source for health information, according to Makovsky, a health communications
People are growing their health-consumer muscles in 2013
Most Americans are concerned about their ability to for medical bills, even when they have health insurance. As a result, most are comfortable asking their doctor about how much their medical treatment will cost. People are becoming savvier health care shoppers largely because they have to: 37% of people in the U.S. have an annual health insurance deductible over $2,000, according to the Spring/Summer 2013 Altarum Institute Survey of Consumer Health Care Opinion, published on 11th July 2013. Many of the media stories coming out of the Altarum survey since its publication have been about people and their trust in
10 Reasons Why ObamaCare is Good for US
When Secretary Sebelius calls, I listen. It’s a sort of “Help Wanted” ad from the Secretary of Health and Human Services Kathleen Sebelius that prompted me to write this post. The Secretary called for female bloggers to talk about the benefits of The Affordable Care Act last week when she spoke in Chicago at the BlogHer conference. Secretary Sebelius’s request was discussed in this story from the Associated Press published July 25, 2013. “I bet you more people could tell you the name of the new prince of England than could tell you that the health market opens October 1st,” the
In the US health care cost game, doctors have seen the enemy – and it’s not them
When it comes to who’s most responsible for reducing the cost of health care in America, most doctors put the onus on trial lawyers, health insurance companies, pharma and medical device manufacturers, hospitals, and even patients. But physicians themselves ? Not so much responsibility – only 36% of doctors polled said doctors should assume major responsibility in reducing health care costs. And, in particular, most U.S. physicians have no enthusiasm for reducing health care costs by changing payment models, like penalizing providers for hospital re-admissions or paying a group of doctors a fixed, bundled price for managing population health. Limiting
What to expect from health care between now and 2018
Employers who provide health insurance are getting much more aggressive in 2013 and beyond in terms of increasing employees’ responsibilities for staying well and taking our meds, shopping for services based on cost and value, and paying doctors based on their success with patients’ health outcomes and quality of care. Furthermore, nearly one-half expect that technologies like telemedicine, mobile health apps, and health kiosks in the back of grocery stores and pharmacies are expected to change the way people regularly receive health care. What’s behind this? Increasing health care costs, to be sure, explains the 18th annual survey from the National
They call it “primary” care because it comes first — and it should
It’s called “primary” care for a reason: it’s first and foremost important in the health care services a person can use. In its report, Primary care: our first line of defense, The Commonwealth Fund explains why primary care is crucial to one’s individual health, and how primary care is morphing into medical teams and patient-centered medical homes. And that’s a good thing for you and me, the Fund says. That’s because people in the U.S. who have a primary care doctor have 33% lower health costs and 19% lower risk of dying than people who see only a specialist (Source:
As health cost increases moderate, consumers will pay more: will they seek less expensive care?
While there is big uncertainty about how health reform will roll out in 2014, and who will opt into the new (and improved?) system, health cost growth will slow to 6.5% signalling a trend of moderating medical costs in America. Even though more newly-insured people may seek care in 2014, the costs per “unit” (visit, pill, therapy encounter) should stay fairly level – at some of the lowest levels since the U.S. started to gauge national health spending in 1960. That’s due to “the imperative to do more with less has paved the way for a true transformation of the
Let patients help: the BMJ covers an American ePatient’s learnings
In this week’s BMJ (British Medical Journal), an American patient tells his story about being equipped, enabled, empowered and engaged — the many “e’s” making up the prefix of “ePatient.” This definition comes out of the work of Dr. Tom Ferguson, who worked with the e-Patient Scholars Working Group in 2007, to publish the first white paper about the phenomenon, e-Patients: how they can help us heal health care. ePatient Dave is the patient-author of the BMJ piece, making the case for shared decision-making and patient involvement in health care decisions. He writes in the conclusion, “The value delivered by skilled
The value of big data in health care = $450 billion
Exploiting Big Data in industry is Big News these days, and nowhere is the potential for leveraging the concept greater than in health care. McKinsey & Company estimates that harnessing big data across five dimensions of health care could yield nearly one-half trillion dollars’ worth of value in The ‘big data’ revolution in healthcare. The chart summarizes McKinsey’s calculations on the value of Big Data in health care at its maximum. Before digging into the value potential, just what is Big Data in health care? Statistics and information are generated in the health care system about patients: say, during visits
U.S. Health Costs vs. The World: Is It Still The Prices, and Are We Still Stupid?
Comparing health care prices in the U.S. with those in other developed countries is an exercise in sticker shock. The cost of a hospital day in the U.S. was, on average, $4,287 in 2012. It was $853 in France, a nation often lauded for its excellent health system and patient outcomes but with a health system that’s financially strapped. A routine office visit to a doctor cost an average of $95 in the U.S. in 2012. The same visit was priced at $30 in Canada and $30 in France, as well. A hip replacement cost $40,364 on average in the
The lights are still out on health prices for Americans – #healthcost transparency limits consumerism in health
Only two U.S. states have comprehensive health care price transparency regulations that ensure citizens’ access to clear and open health price information. While those two states, Massachusetts and New Hampshire, earn an “A” in the Report Card on State Price Transparency Laws, an addition five state earn a “B,” with the remainder of the United States garnering a “C” or less. The map illustrates that most states are red states, earning the lowest score of “F.” With the growth of high-deductible health plans (under the umbrella of so-called “consumer-directed” plans) where health consumers pay thousands of dollars to meet a spending
Do doctors want patients to have full access their own medical information? It depends.
Only one-third of U.S. physicians believe that patients should have “full access” to their electronic health records, according to Patient Access to Electronic Health Records What Does the Doctor Order?, a survey conducted by Accenture, released at HIMSS13 in March 2013. Two-thirds of doctors in the U.S. are open to patients having “limited access” to their EHRs. However, the extent to which doctors believe in full EHR access for patients depends on the type of health information contained in the record. Accenture surveyed 3,700 physicians in eight countries: Australia, Canada, England, France, Germany, Singapore, Spain and the United States, and found the doctors’
A health economics lesson from Jonathan Bush, at the helm of athenahealth
At HIMSS13 there are the equivalent of rock stars. Some of these are health system CIOs and health IT gurus who are driving significant and positive changes in their organizations, like Blackford Middleton, Keith Boone, Brian Ahier, and John Halamka. Others are C-level execs at health IT companies. In this latter group, many avoid the paparazzi (read: health trade reporters) and stay cocooned behind closed doors in two-story pieces of posh real estate on the exhibition floor. A few walk the floor, shake hands with folks, and take in the vibe of the event. We’ll call them open-source personalities. The
Patients globally would embrace Jetsons-style health care…but will health providers?
Patients are getting comfortable with remote health care – that is, receiving care from a health provider at a distance via, say, telehealth or via a Skype-type of set-up. Furthermore, 70% of people globally saying they would trust an automated device to provide a diagnosis that would help them determine whether or note they needed to see a doctor. Based on the findings from Cisco‘s survey summarized in the Cisco Connected Customer Experience Report – Healthcare, published March 4, 2013, just-in-time for the annual 2013 HIMSS conference, a majority patients the world over are embracing health care delivered via communications
The Accountable Care Community opportunity
“ACOs most assuredly will not…deliver the disruptive innovation that the U.S. health-care system urgently needs,” wrote Clay Christensen, godfather of disruptive innovation, et. al., in an op-ed in the Wall Street Journal of February18, 2013. In the opinion piece, Christensen and colleagues make the argument that Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) as initially conceived won’t address several key underlying forces that keep the U.S. health care industry in stasis: Physicians’ behavior will have to change to drive cost-reduction. Clinicians will need “re-education,” the authors say, adopting evidence-based medicine and operating in lower-cost milieus. Patients’ behavior will have to change. This requires
Required reading: TIME Magazine’s Bitter Pill Cover Story
Today’s Health Populi is devoted to Steven Brill and his colleagues at TIME magazine whose special report, Bitter Pill: Why Medical Bills Are Killing Us, is required reading for every health citizen in the United States. Among many lightbulb moments for readers, key findings from the piece are: Local hospitals are beloved charities to people who live in their market – Brill calls these institutions “Non-Profit Profitmakers). They’re the single most politically powerful player in most Congressional districts The poor and less affluent more often pay the high chargemaster (“retail list”) price for health products and services vs. the wealthy
Physicians like mobile health apps for patient health – eClinicalWorks on transformational path
A vast majority – 9 in 10 physicians – like mobile health (mHealth) apps, especially when tied to electronic health records (EHRs). eClinicalWorks surveyed physicians in January 2013, and found physicians bullish on mobile health apps for patient benefit – not just for their own office productivity and workflow. Specifically, – 93% of physicians say mobile health apps can improve patients’ health outcomes – 89% of physicians would recommend an mHealth app to a patient – 58% of doctors note a key mHealth benefit is providing patients with appointment alerts and reminders – 2 in 3 physicians say mHealth apps
Physician workflow: barrier to consumer health engagement?
This week, I had a conversation with a physician whom I consider quite patient-engaged, who uses an EHR, and who works with one of the most wired health organizations in the United States. I complained to her that my user-generated data from my Bodymedia armband, Fitbit, Withings scale, among other #QuantifiedSelf devices, can’t find their way through the cloud to my doctors’ electronic health records or my patient portal. Her reaction was surprising to me. She was not so keen on the idea, saying, “It’s the physician workflow” that’s the problem. The wordle on workflow comes from Dr. Chuck Webster
Butter over guns in the minds of Americans when it comes to deficit cutting
Americans have a clear message for the 113th Congress: I want my MTV, but I want my Medicare, Medicaid, Social Security, health insurance subsidies, and public schools. These budget-saving priorities are detailed in The Public’s Health Care Agenda for the 113th Congress, conducted by the Kaiser Family Foundation, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, and the Harvard School of Public Health, published in January 2013. The poll found that a majority of Americans placed creating health insurance exchanges/marketplaces at top priority, compared with other health priorities at the state level. More people support rather than oppose Medicaid expansion, heavily weighted toward 75%
Health reform, costs and the growing role of consumers: PwC’s tea leaves for 2013
PwC has seen the future of health care for the next year, and the crystal ball expects to see the following: Affordable Care Act implementation, with states playing lead roles The role of dual eligibles Employer’s role in health care benefits Consumers’ role in coverage Consumers’ ratings impact on health care Transforming health delivery Population health management Bring your own device Pharma’s changing value proposition The medical device industry & tax impact. In their report, Top health industry issues of 2013: picking up the pace on health reform, PwC summarizes these expectations as a “future [that] includes full implementation of
Think about health disparities on Martin Luther King Day 2013
On this day celebrating Martin Luther King, Jr., I post a photo of him in Detroit in 1963, giving a preliminary version of his “I Have a Dream” speech he would give two months later in Washington, DC. As I meditate on MLK, I think about health equity. By now, most rational Americans know the score on the nation’s collective health status compared to other developed countries: suffice it to say, We’re Not #1. But underneath that statistic is a further sad state of health affairs: that people of color in the U.S. have lower quality of health than white
Retail and work-site clinics – medical homes for younger adults?
The use of retail and work-site health clinics is up, and their consumers skew young. Overall, 27% of all U.S. adults have stepped into a walk-in clinic in the past two years. But only 15% of people 65 and over have used such a clinic. This begs the question: are retail and on-site clinics at the workplace filling the role of medical homes for younger adult Americans? The Harris Interactive/HealthDay poll published in January 2013 discovered that use of retail clinics grew from 7% in 2008 to 27% in 2012. The largest age cohort using walk-in clinics is people between
Cost-conscious health consumers are adopting personal health IT
People enrolled in consumer-directed health plans (CDHPs) and high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) are more cost-conscious than those enrolled in more traditional plans, according to Findings from the 2012 EBRI/MGA Consumer Engagement in Health Care Survey from the Employee Benefit Research Institute (EBRI), published in December 2012. The logic behind CDHPs and HDHPs is that if health plan enrollees have more “skin in the game” — that is, personal financial exposure — they’ll behave more like health “consumers.” By 2012, 36% of employers with over 500 employees offered either HRA- or HSA-eligible plans. About 15% of working age adults are enrolled
Consumers want digital communications from providers, from payment reminders to patient care via email
85% of U.S. health consumers say that emails, text messages, and voicemails are at least as helpful as in-person or phone conversations with health providers, according to the TeleVox Healthy World study, Technology Beyond the Exam Room. The study was based on surveys conducted with over 2,200 health providers across specialties, and 1,015 U.S. adults over 18. Furthermore, one in 3 consumers admit to being more honest when talking about medical needs via automated voice response systems, emails or texts than face-to-face with a health provider. And 3 in 10 consumers believe that receiving digital health communications from providers such
Physicians’ growing use of the Internet: where trust and value drive information search
“The Internet will have a profound effect on the practice and business of medicine. Physicians, eager to provide high-quality care and forced by competition to offer online services, will introduce e-mail and patient-friendly Web sites to improve administrative services and manage common medical conditions. Patients will identify more helath information online and will take more responsibility for their care. The doctor/patient relationship will be altered. Some aspects of electronic communication will enhance the bond, and others will threaten it. Patients will have access to vast information sources of variable validity. Many physician organizations are preparing for the electronic transformation, but
The physician time-squeeze and burnout: just-in-time information is part of the solution
One in two doctors is burned out. Physicians are seeing more patients in a day and spend less time with each of them. This leads to job burnout, and greater probability for medical errors and eventual liability challenges, along with feeling pushed toward early retirement. In a study published in August 2012 in the Archives of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic researchers learned that physicians are more burned out than workers in any other profession. And those at greatest risk of “being on a hamster wheel,” as Dr. Jeff Cain, president-elect of the American Academy of Family Physicians describes the scenario, are primary
Nurses, pharmacists and doctors rank top in honesty, says Gallup poll
Nurses, pharmacists and doctors rank tops with Americans when it comes to honesty and ethics. Most people also rate engineers, dentists, police officers, clergy and college teachers as high on honesty metrics. Lawmakers (THINK: Congress) and car salesman fall to the bottom of the honesty-and-trust roster, who only 1 in 10 Americans believe act with honesty and integrity. Other low-ranking professions on this list are HMO managers, stockbrokers, and folks in the advertising business. Welcome to this year’s Gallup Poll on consumers’ perceptions of honesty and ethics in 22 professions in the U.S. Gallup measures six health care professions
Americans #1 health care priority for the President: reduce costs
Reducing health care costs far outranks improving quality and safety, improving the public’s health, and upping the customer experience as Americans’ top priority for President Obama’s health care agenda, according to a post-election poll conducted by PwC’s Health Research Institute. In Warning signs for health industry, PwC’s analysis of the survey results, found that 7 in 10 Americans point to the high costs of health care as their top concern in President Obama’s second term for addressing health care issues. Where would cost savings come from if U.S. voters wielded the accountant’s scalpel? The voters have spoken, saying, Reduce payments
No digital divide among doctors: technology enables a majority of doctors to learn and go social
Health care professionals (HCPs) have adopted smartphones and tablets faster than the man-and-woman-on-the-street. As a result, mobile devices have become an all-important channel for communicating information to all clinicians: doctors, nurses and pharmacists. Today, medical practice is “done” via computers: the chart, from MedPage Today’s survey of physicians conducted in July 2012, shows that 100% of doctors get their learning via desktop and laptop computers (THINK: continuing medical education, for example). 88% of doctors go social online, including using point-of-care tools based on MedPage’s definition of “social interactions.” 9 in 10 doctors have increased the use of the internet in
Consumers blame insurance and pharma for health costs, but love their primary care doctors
The 78% of U.S. adults with primary care physicians (think: medical homes) are very satisfied with their doctors’ visits. The main reasons for this high level of satisfaction include communication (listening, talking), customer service (caring, personable), and clinical (good diagnosis and treatment). More women than men have a primary care physician relationship, more college grads do, and more people with incomes of $75,000 a year or more do, as well. 90% of those 55 and over have a primary care doctor – a stat heavily influenced by the fact that Medicare coverage kicks in for older people. This consumer profile
Elsevier’s ClinicalKey Hits the Road – a mobile healthcare search tour
There are many definitions of mobile health, and Elsevier is adding another to the list. The world’s largest medical publisher has taken its new clinical search tool, ClinicalKey, on the road. Coined the ClinicalKey Experience Tour, Elsevier is coming to a medical center near you to enable clinicians, medical librarians, and health care administrators to give ClinicalKey a spin in their hospital’s parking lot. The challenge: the amount of new medical information doubles every 5 years, while 4 in 5 physicians say they have less than five hours a month to keep up with this, according to a DoctorDirectory survey. At the same time, health care providers feel hard-pressed
In sickness and in health: consumers expect doctors to be wellness coaches, too
4 in 5 health consumers expect doctors not only to treat them when they’re sick, but to keep them healthy. “In sickness and in health” now morphs over to the doctor-patient relationship, beyond the marriage vow. Better Health through Better Patient Communications, a survey from Varolii, finds that people are looking for health, beyond health care, from their physicians. Varolii is a customer interaction company that claims to have interacted with 1 in 3 Americans through some sort of company communication: they work with major Fortune 1000 companies, including banks, airlines, retail, and, yes, health care. They recently attracted a
From fragmentation and sensors to health care in your pocket – Health 2.0, Day 1
The first day of the Health 2.0 Conference in San Francisco kicked off with a video illustrating the global reach of the Health 2.0 concept, from NY and Boston to Mumbai, Madrid, London, Tokyo and other points abroad. Technology is making the health world flatter and smarter…and sometimes, increasing problematic fragmentation, which is a theme that kept pinching me through the first day’s discussions and demonstrations. Joe Flowers, health futurist, offered a cogent, crisp forecast in the morning, noting that health care is changing, undergoing fundamental economic changes that change everything about it. These are driving us to what may
3 in 5 physicians would quit today if they could
Being a doctor isn’t a happy profession in 2012: 3 in 5 doctors say that, if they could, they’d retire this year. Over three-fourths of physicians are pessimistic about the future of their profession. 84% of doctors feel that the medical profession is in decline. And, over 1 in 3 doctors would choose a different professional if they had it all to do over again. The Physicians Foundation, a nonprofit organization that represents the interests of doctors, sent a survey to 630,000 physicians — every physician in the U.S. that’s registered with the AMA’s Physician Master File — in March-June





 I'm in amazing company here with other #digitalhealth innovators, thinkers and doers. Thank you to Cristian Cortez Fernandez and Zallud for this recognition; I'm grateful.
I'm in amazing company here with other #digitalhealth innovators, thinkers and doers. Thank you to Cristian Cortez Fernandez and Zallud for this recognition; I'm grateful. Jane was named as a member of the AHIP 2024 Advisory Board, joining some valued colleagues to prepare for the challenges and opportunities facing health plans, systems, and other industry stakeholders.
Jane was named as a member of the AHIP 2024 Advisory Board, joining some valued colleagues to prepare for the challenges and opportunities facing health plans, systems, and other industry stakeholders.  Join Jane at AHIP's annual meeting in Las Vegas: I'll be speaking, moderating a panel, and providing thought leadership on health consumers and bolstering equity, empowerment, and self-care.
Join Jane at AHIP's annual meeting in Las Vegas: I'll be speaking, moderating a panel, and providing thought leadership on health consumers and bolstering equity, empowerment, and self-care.