Pharma and the health industry: when will they finally meet us Where We Live?
Millions of health citizens, consumers, patients and caregivers flock to Facebook, Twitter and Wikipedia every day the world over to seek health information, advocate for patients’ access to a cancer therapy on a health blog, engage in peer-to-peer health care in a social network, and bolster each others’ management of chronic medical conditions in a chat community. Yet the pharmaceutical and medical device industries rank well behind other industries vis-à-vis the use of social media, asserts Engaging patients through social media, with the punchline question: is healthcare ready for empowered and digitally demanding patients? from the IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics, published on
Do People Really Want To Tech Their Health? in Huffington Post
This post appeared in my Huffington Post column on January 16, 2013. In the afterglow of the 2014 Consumer Electronics Show (CES), away from the neon lights of Las Vegas, 4D curved TV screens, and uber-hip Google Glass wearers, a big question remains: Do we, the people, really want to tech our way to self-health? The number of digital health companies exhibiting at CES grew by 40 percent, exceeding 300 based on the count of the International Consumer Electronics Association, sponsor of the event. The hockey-stick growth of “wearable technology” seen at the 2014 Consumer Electronics Show begs the question: Are there
Health costs and wellness: can digital tools bridge the gap? Altarum’s Fall 2013 consumer survey
More than twice as many people value the opinions of friends and family for health care provider choices than turn to online ratings for doctors’ bedside manner, waiting times, or clinical quality, according to the Altarum Institute Survey of Consumer Health Care Opinions, Fall 2013, released on January 8, 2014. 1 in 3 consumers also looks into the cost and quality of services recommended by nurses, doctors, labs and hospitals before choosing a provider. However, most people (4 in 5) say they are comfortable asking their doctor about how much treatment will cost: 43% are “very comfortable,” and 38% somewhat comfortable,
Health Care Everywhere at the 2014 Consumer Electronics Show
When the head of the Consumer Electronics Association gives a shout-out to the growth of health products in his annual mega-show, attention must be paid. The #2014CES featured over 300 companies devoted to “digital health” as the CEA defines the term. But if you believe that health is where we live, work, play, and pray, then you can see health is almost everywhere at the CES, from connected home tech and smart refrigerators to autos that sense ‘sick’ air and headphones that amplify phone messages for people with hearing aids, along with pet activity tracking devices like the Petbit. If
4 in 10 Americans keen to buy an app or device for health/fitness: Accenture’s 2014 digital lifestyle survey
Wearable technology is the new fashion accessory, Accenture observes in its 2014 survey report, Racing Toward a Complete Digital Lifestyle: Digital Consumers Crave More. In parallel with the supply-side growth of wearable technology that is seen this week at the 2014 Consumer Electronics Show, Accenture brings a sanguine story to the supply side of the equation, finding consumers “craving more” than one function from a digital device. Over one-half of consumers surveyed in six countries favored vehicle navigation, home safety/security monitors, health monitor, home comfort and control, fitness monitors, and personal safety monitors. Nearly one half (46%) liked smartwatches, and
Health is everywhere – seeing health in JWT’s Top 100 Trends for 2014
Of 100 broad-based trends to expect in 2014, most relate in some way to health. I’ve reviewed every one of the 100 forecast points in JWT’s 100 Things to Watch in 2014 report, and it seems Health is Everywhere. Let me point out many, which I’ve allocated to health-ified buckets (note that JWT organizes the list of 100 by alphabet, from “A” to “Z,” so they are not in any prioritized or strategic order). The most direct-health impacting bucket of trends are those in health tech. These include E-cigarette regulation (#35), Glassware (#42), Haptic technology (#46), Needle-free vaccines (#64), Oculus Rift (#65), OTT TV (#66), Telediagnostics
mHealth will join the health ecosystem – prelude to the 2014 Consumer Electronics Show
The rise of digital health at the 2014 Consumer Electronics Show signals the hockey-stick growth of consumer-facing health devices for fitness and, increasingly, more medical applications in the hands of people, patients, and caregivers. This year at #CES2014, while the 40% growth of the CES digital health footprint will get the headlines, the underlying story will go beyond wristbands and step-tracking generating data from an N of 1 to tools that generate data to bolster shared-decision making between people and the health system, and eventually support population health. For example: – Aetna is partnering with J&J to deploy their Care4Today
3 Things I Know About Health Care in 2014
We who are charged with forecasting the future of health and health care live in a world of scenario planning, placing bets on certainties (what we know we know), uncertainties (what we know we don’t know), and wild cards — those phenomena that, if they happen in the real world, blow our forecasts to smithereens, forcing a tabula rasa for a new-and-improved forecast. There are many more uncertainties than certainties challenging the tea leaves for the new year, including the changing role of health insurance companies and how they will respond to the Affordable Care Act implementation and changing mandates
Don’t over-forecast mobile health in the short-run
The 2013 Mobile Health Summit was hosted by HIMSS at The Gaylord Resort in suburban Washington DC, taking place over 4 days during the mid-atlantic region’s iciest conditions in years. But inside the cocoon of this convention space, 5,000 conveners took in demonstrations of innovations using mobile platforms and standards that extend health services, knowledge and self-help tools to people and providers. Several themes emerged out of the meeting… Lots of apps, too few business models. There are too many apps and not enough companies, Esther Dyson noted in a keynote session during which she dialogued with two Steve’s: Steven
Data altruism: people more likely to share personal health data for the sake of others and to save money
While about 53% of people globally are willing to share various types of personal data overall, the kind of data willing-to-be-shared varies by type of information — and what country we’re from. When asked how likely they would be to anonymously share information if it could lead to improvements or innovations in that technology, Americans are less likely to be willing to share any type of personal data — except for gender. When it comes to sharing several specific types of health information, fewer Americans are likely to want to share it as Intel found in their survey published in the company’s Healthcare
More chronically ill people use online health resources – but they’re not so social, Pew finds
People who are diagnosed with at least one chronic medical condition are more likely to seek information online, use social media to understand peer patients’ reviews on drugs and treatments, and learn from other patients about their personal health experiences. While that’s encouraging news for a health empowerment headline, the underlying challenge that should prevent congratulatory fist-bumps among patient-engagement proponents is that people living with chronic disease are less likely to have internet access. Why? Because chronically ill people tend to be older and less educated, and they’re also less likely to be working. Simply put, “People living with chronic
Self-service health – how consumers can help solve the primary care shortage
Self-service – people DIYing health care — can help solve the primary care shortage in America, based on the findings of 23 studies published this week. If health information technologies (health IT) were “fully implemented” in 30% of doctors’ offices, demand for physicians would fall by 4 to 9%, according to The Impact of Health Information Technology and e-Health On the Future Demand for Physician Services, published in the November 2013 issue of Health Affairs. Weiner, Yeh and Blumenthal did a meta-analysis of the literature on health IT and its potential to improve productivity and extend physician services and found
Mobile health apps – opportunity for patients and doctors to co-create the evidence
There are thousands of downloadable apps that people can use that touch on health. But among the 40,000+ mobile health apps available in iTunes, which most effectively drive health and efficient care? To answer that question, the IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics analyzed 43,689 health, fitness and medical apps in the Apple iTunes store as of June 2013. These split into what IMS categorized as 23,682 “genuine” health care apps, and 20,007 falling into miscellaneous categories such as product-specific apps, fashion and beauty, fertility, veterinary, and apps with “gimmicks” (IMS’s word) with no obvious health benefit. Among the 23,682 so-called
Getting to health engagement will require more than a patient portal
Patient and health engagement is the flavor du jour in health circles these days, from the corridors of hospitals to the caffeinated marketing meetings in Big Pharma’s east coast meet-ups. But there’s no standard agreement on what we mean by peoples’ health engagement, whether by patient or well consumer. In Market Insights: The Evolution of Consumer Engagement in Health Care, Porter Research endeavors to deepen our understanding of this important concept. In the introductory section of the paper, “Understanding Engagement,” Porter proffers that industry – providers, payers and employers – consider engagement as “changing consumer behavior through increased participation in consumers’ own health
Innovating and thriving in value-based health – collaboration required
In health care, when money is tight, labor inputs like nurses and doctors stretched, and patients wanting to be treated like beloved Amazon consumers, what do you do? Why, innovate and thrive. This audacious Holy Grail was the topic for a panel II moderated today at the Connected Health Symposium, sponsored by Partners Heathcare, the Boston health system that includes Harvard’s hospitals and other blue chip health providers around the region. My panelists were 3 health ecosystem players who were not your typical discussants at this sort of meeting: none wore bow ties, and all were very entrepreneurial: Jeremy Delinsky
Consumers trust and welcome health and insurance providers to go DTC with communications
Consumers embrace ongoing dialog with the companies they do business with, Varolii Corporation toplines in a survey report, What Do Customers Want? A Growing Appetite for Customer Communications. Across all vertical industries consumers trust for this dialogue, health care organizations – specifically doctors, pharmacists, and insurance companies – are the most trusted. Examples of “welcome-comms” would be reminders about upcoming appointments or vaccinations (among 69% of people), notices to reorder or pick up a prescription (57%), and messages encouraging scheduling an appointment (39%). In banking, notices about fraudulent activity on one’s account is the most welcomed message beating out appointment
Health care and survey taking at the Big Box Store
Where can you shop the health and beauty aisles, pick up some groceries and a prescription, get a flu vaccine, and weigh in on Obamacare and what digital health tools you like? Why, at one of several thousand retail stores where you can find a SoloHealth kiosk. As of yesterday afternoon, over 32 million encounters were recorded on SoloHealth kiosks, based on an app I saw on the company CEO Bart Foster’s smartphone. Kiosks are locatted around the United States in retailers including Walmart and Sam’s Clubs, along with major grocery chains like Schnuck’s and Publix, and the CVS pharmacy
The FDA Has Spoken, and It Will Regulate “Some” mHealth Apps
The FDA has spoken: there are 2 statutory definitions for a mobile health tool as a “medical device” that the Agency says it has regulatory oversight: To be used as an accessory to a regulated medical device, or To transform a mobile platform into a regulated medical device. On page 8 of the Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff, you can read the FDA’s expanded definition of a mobile health app as being: “…intended for use in performing a medical device function (i.e. for diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or the cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention
Healing the Patient-Doctor Relationship with Health IT
A cadre of pioneering Americans has been meaningfully using personal health information technology (PHIT), largely outside of the U.S. health care system. These applications include self-tracking and wearable health technologies, mobile health apps, and digital medical tracking devices like glucometers that streamline tracking and recording blood glucose levels. In the meantime, only 21% of doctors surveyed by Accenture currently allow patients to have online access to their medical summary or patient chart – very basic components of the electronic health record. We know what’s primarily driving health providers’ adoption of health IT: namely, the HITECH Act’s provisions for incentives. But
Defining Mobile Health – the blur between health and health care
Mobilising Healthcare, a new report from Juniper Research, segments the mobile health sector into “healthcare” and “health & fitness” segments. The research summary notes that fitness is a relatively new market compared with health “care,” which has been around for eons. Fitness, the analysts say, “is exempt from government intervention.” Mobile healthcare (“mHealth”) applications explored include SMS health messaging, remote health provision such as cardiac monitoring, electronic health records and personal health records. In mFitness, Juniper looks into mobile tech for athletes and fitness conscious people, and activity tracking including heart function, distance, respiration, and perspiration, among other parameters. mHealth
Health information search online, an hour a week. Time with a doctor? An hour a year.
In game-scoring unit terms, 52 is the number of hours an average American spends seeking health information online each year. The 1 (hour) is roughly equivalent to the approximate total time a patient spends with a physician (an average of 3 visits, with an average time per vision of 20 minutes). Thus, 52:1. This means that the average U.S. health consumer spends much more time DIYing her health using digital information resources than speaking face-to-face with their physician in the doctor’s office. Still, the physician continues to be a go-to source for health information, according to Makovsky, a health communications
People with doctors interested in EMRs, but where’s the easy button?
1 in two people who are insured and have a regular doctor are interested in trying out an electronic medical record. But they need a doctor or nurse to suggest this, and they need it to be easy to use. The EMR Impact survey was conducted by Aeffect and 88 Brand Partners to assess 1,000 U.S. online consumers’ views on electronic medical records (EMRs): specifically, how do insured American adults (age 25 to 55 who have seen their regular physician in the past 3 years) view accessing their personal health information via EMRs? Among this population segment, 1 in 4 people (24%)
Needing a new kind of tracker to track #mhealth investments in 2013
The news this week that Fitbit attracted $42 million investment capital follows Withings’ announcement of $30 million (including Euro11 million from BPIFrance, the French national investment fund), Jawbone’s recent acquisition of Bodymedia for $100 million in April 2013, and MyFitnessPal raising $13 million earlier this month. The quick arithmetic for these four companies alone adds to roughly $200 mm in a few months going to these brands, which are feverishly competing for the heartbeats and footsteps of people who are keen to track their steps and stay healthy. Can you keep up? You need a new kind of activity tracker to track
Americans’ health insurance illiteracy epidemic – simpler is better
Consumers misunderstand health insurance, according to new research published in the Journal of Health Economics this week. The study was done by a multidisciplinary, diverse team of researchers led by one of my favorite health economists, George Loewenstein from Carnegie Mellon, complemented by colleagues from Humana, University of Pennsylvania, Stanford, and Yale, among other research institutions. Most people do not understand how traditional health plans work: the kind that have been available on the market for over a decade. See the chart, which summarizes top-line findings: nearly all consumers believe they understand what maximum out-of-pocket costs are, but only one-half do.
Happy today, nervous about health and money tomorrow: an Aging in America update
Most older Americans 60 years of age and up (57%) say the last year of their lives has been “normal” – a large increase from the 42% who said life was normal in 2012. And nearly 9 in 10 older Americans are confident in their ability to maintain a high quality of life in their senior years. The good news is that seniors are maintaining a positive outlook on aging and their future. The downside: older people aren’t doing much to invest in their future health for the long run. They’re also worried about the financial impact of living longer.
People are growing their health-consumer muscles in 2013
Most Americans are concerned about their ability to for medical bills, even when they have health insurance. As a result, most are comfortable asking their doctor about how much their medical treatment will cost. People are becoming savvier health care shoppers largely because they have to: 37% of people in the U.S. have an annual health insurance deductible over $2,000, according to the Spring/Summer 2013 Altarum Institute Survey of Consumer Health Care Opinion, published on 11th July 2013. Many of the media stories coming out of the Altarum survey since its publication have been about people and their trust in
Google, your new-tritionist
Your new-nutritionist is now Google, which launched a nutrition utility through Google Search. “From the basics of potatoes and carrots to more complex dishes like burritos and chow mein, you can simply ask, ‘How much protein is in a banana?’ or ‘How many calories are in an avocado?’ and get your answer right away,” the official Google Search blog explains. Over 1,000 items – fruits, vegetables, meats, dairy items, and prepared meals like Chinese and Mexican take out, as mentioned in Google’s quote above – are searchable via web and mobile, powered by Google’s Knowledge Graph. The Knowledge Graph is the
Health and wellness, the economy and the grocery store
Consumers in America are spending more, and especially at the grocery store. Most people say they want to eat healthy — but, although they’re spending more at the food store, one-half of supermarket shoppers say cost is the main obstacle for healthy eating. 2 in 3 U.S. grocery shoppers define health and wellness as being physically fit and active, and over half believe that feeling good about yourself is another facet of health. Not being overweight equals health for about one-half of U.S. shoppers. The Why? Behind the Buy, from Acosta Sales & Marketing, explores buying patterns among U.S. consumers
How mobile phones bring good things to life (and health)
…and I’m not talking about GE here (or here). Most people (75%) still view phone calls as the communication mode that best bolsters their relationships compared with texting (66%), picture messaging (35%), sharing on social networks (31%), emailing (25%), , and video chatting (9%). U.S. Cellular, the mobile phone company, surveyed 527 customers in April 2013 to learn about how wireless communication can bring “Better Moments” to peoples’ lives. In particular, people say that mobile phones help them: Communicate more frequently (77%) Share experiences right away (66%) Share moments that would have otherwise been missed (52%). 9 in 10 people take pictures on
1 in 3 people is interested in doing mobile health, but they skew younger
The headline for the HarrisInteractive/HealthDay mobile health (mHealth) survey reads, “Lots of Americans Want Health Care Via Their Smartphones.” But underneath that bullish forecast are statistics illustrating that the heaviest users of health care services in America — people 65 and over — have the least interest in mHealth tools. Overall, 37% of U.S. adults are interested in managing health via smartphones or tablets: about 1 in 3 people. As the chart shows, the greatest interest in communicating with doctors via mobile phones and tablets is among people 25-49. Reminders to fill prescription and participate in wellness programs is also
The emerging economy for consumer health and wellness
The notion of consumers’ greater skin in the game of U.S. health care — and the underlying theory of rational economic men and women that would drive people to greater self-care — permeated the agenda of the 2nd annual Consumer Health & Wellness Innovation Summit, chaired by Lisa Suennen of Psilos Ventures. Lisa kicked off the meeting providing a wellness market landscape, describing the opportunity that is the ‘real’ consumer-driven health care: people getting and staying well, and increasing participation in self-management of chronic conditions. The U.S. health system is transforming, she explained, with payors beginning to look like computer
Driving innovation in health through the use of open data: Health Datapalooza, Year 4
In the $3 trillion economy that is American health care, the role of information technology is central to transforming this huge piece of U.S. fiscal activity. This week convened the fourth annual Health Datapalooza (HDP) in Washington DC, with the underlying theme, “health engagement is the blockbuster drug of the 21st century” (quoting Leonard Kish). This meeting of over 2,000 registrants – huge growth from the first year’s 400 attendees — is organized by the Health Data Consortium (HDC) , whose CEO Dwayne Spradlin kicked off remarks on Day 2 of HDP4. He described the HDC, a public-private collaboration led
The physician-consumer health IT chasm: most doctors lagging in online patient support tools
In the long-run, health information technology (HIT) will improve the quality of health care, according to 73% of U.S. physicians. However, about the same number (7 in 10 physicians) believe that the ROI on health IT is inflated and that implementing EHRs will cost more, not less. Still, market forces from health insurance plans, payers and consumers are driving health IT adoption, according to Deloitte’s survey report, Physician adoption of health information technology: implications for medical practice leaders and business partners. Electronic health records (EHR) adoption and meeting meaningful use (MU) Stage 1 criteria appears strongly related to the size
Marketing Digital Health to Mom 2.0 on Mother’s Day 2013
Mainstream media, both print and online, peppered their 2013 Mother’s Day gift suggestions including pod coffeemakers, bangle bracelets, candy-colored accessories and digital health devices. Say, what? In Parade magazine, Mother’s Day 2013 gift ideas included the Fitbit “smart pedometer,” linked to a “buy” site at REI. You can’t get much more mainstream than Parade. In Entertainment Weekly, Bronwyn Barnes, style maven for the magazine, wrote a one-page “Get Ready for Mom 2.0” and her recommendations included the Pebble Smartwatch, the Jawbone Up wristband, and the HoodieBuddie with earbuds built into the drawstrings. Men’s Health told sons and husbands to check
FDA goes DTP(atient)
The Food & Drug Administration (FDA) launched its new website for and about patients, the Patient Network, with the tagline, “Bringing your voice to drug and device approval and safety.” With this move, the FDA moves toward social health, someplace where at least one-third of U.S. consumers already opine, shop, share personal info, crowdsource cures, and support each other on all-matters-health-and-illness. The objective of the Patient Network is, “to help FDA help patients have a bigger voice.” Dr. Margaret Hamburg, the Commissioner of the FDA, talks about the concept here. The rationale? “When patients better understand the intricacies of how
The need for a Zagat and TripAdvisor in health care
Patient satisfaction survey scores have begun to directly impact Medicare payment for health providers. Health plan members are morphing into health consumers spending “real money” in high-deductible health plans. Newly-diagnosed patients with chronic conditions look online for information to sort out whether a generic drug is equivalent to a branded Rx that costs five-times the out-of-pocket cost of the cheaper substitute. While health care report cards have been around for many years, consumers’ need to get their arms around relevant and accessible information on quality and value is driving a new market for a Yelp, Travelocity, or Zagat in
The value of big data in health care = $450 billion
Exploiting Big Data in industry is Big News these days, and nowhere is the potential for leveraging the concept greater than in health care. McKinsey & Company estimates that harnessing big data across five dimensions of health care could yield nearly one-half trillion dollars’ worth of value in The ‘big data’ revolution in healthcare. The chart summarizes McKinsey’s calculations on the value of Big Data in health care at its maximum. Before digging into the value potential, just what is Big Data in health care? Statistics and information are generated in the health care system about patients: say, during visits
Walgreens Steps with Balance program rewards both consumers and the store
Consumers who patronize Walgreens can get rewarded for tracking their physical activity For the Steps with Balance program kickoff, self-tracking consumers can earn 20 points for every mile walked or run and 20 points for tracking weight. Walgreens implemented the Walk with Walgreens program in 2012. The program won an Effie Award for an outstanding marketing program. With the success of Walk with Walgreens, the retail pharmacy company has expanded the program beyond simple steps to include weight tracking and health goals for earning loyalty points. The program enables a few of the most popular self-tracking devices to sync so
An American Nanny State? Most Americans support government tactics addressing lifestyle impacts on chronic disease
Most people like government policies targeting reducing tobacco use, requiring food manufacturers and restaurants to reduce salt content, and mandating schools to require 45 minutes of daily activity for students. A large majority of Americans (at least 8 in 10 people) support government actions to promote public health that stem chronic disease, from preventing cancer (89%) and heart disease (86%) to helping people control their diabetes (84%) and preventing childhood obesity (81%). A Survey Finds Public Support For Legal Interventions Directed At Health Behavior To Fight Noncommunicable Disease (NCD). This poll, published in the March 2013 issue of Health Affairs, profiles the
The lights are still out on health prices for Americans – #healthcost transparency limits consumerism in health
Only two U.S. states have comprehensive health care price transparency regulations that ensure citizens’ access to clear and open health price information. While those two states, Massachusetts and New Hampshire, earn an “A” in the Report Card on State Price Transparency Laws, an addition five state earn a “B,” with the remainder of the United States garnering a “C” or less. The map illustrates that most states are red states, earning the lowest score of “F.” With the growth of high-deductible health plans (under the umbrella of so-called “consumer-directed” plans) where health consumers pay thousands of dollars to meet a spending
Do doctors want patients to have full access their own medical information? It depends.
Only one-third of U.S. physicians believe that patients should have “full access” to their electronic health records, according to Patient Access to Electronic Health Records What Does the Doctor Order?, a survey conducted by Accenture, released at HIMSS13 in March 2013. Two-thirds of doctors in the U.S. are open to patients having “limited access” to their EHRs. However, the extent to which doctors believe in full EHR access for patients depends on the type of health information contained in the record. Accenture surveyed 3,700 physicians in eight countries: Australia, Canada, England, France, Germany, Singapore, Spain and the United States, and found the doctors’
Gettin’ higi with it: Lupe Fiasco’s foray into public health
The latest in SoLoMo (Social, Local, Mobile) Health is a gamified tool coupled with a hardware kiosk, known as higi. The brainchild of Michael Ferro, a successful dotcom entrepreneur who now owns the Chicago Sun-Times, higi’s mission is to help people – particularly younger peeps – to take better care of themselves by scoring points and, as a result, social connections. Higi’s an African word for origin, so the health tool has some aspects relating to being in a tribe — a kind of health tribe. It also has a fun sound to it, Ferro noted, which sets the vibe
Health at SXSW13 vs. HIMSS13: the Yin, the Yang, and the Blur
I endured what very few people could (or would) do in the past ten days: I traveled to New Orleans to the annual conference of HIMSS, the Health Information Management Systems Society, which features hundreds of suppliers to the health care information technology industry. I returned home to kiss my family hello and goodbye, and a day later flew to Austin for the annual South-by-Southwest conference for music, movie and digital folks. The health track at SXSW has grown over the past five years, and provides a start contrast to “health care” as embodied at HIMSS, and “health” translated through
The Sitting Disease: health is growing at SXSW
If it’s March, it must be time for South by Southwest (SXSW), the annual conference weaving music, film and interactive tracks of speakers and conferees that overcrowds and excites Austin, Texas, with a cool vibe and even cooler ideas. I’ll be participating on Sunday 10 March 2013 at 5 pm on a panel, Sitting Will Kill You: Can Mobile Save Us?, featuring Fran Melmed, developer of the HotSeat app that nudges us to all Get Up Offa Our Things when living our typical sedentary lives; Peter Katzmarzyk, public health researcher who knows all about the relationship between too much sitting
Eric Topol creatively destroys medicine at #HIMSS13
Wearing his Walking Gallery jacket painted by (im)patient advocate, Regina Holliday, Dr. Eric Topol evangelized the benefits of digital medicine and consumer empowerment in health care, largely summarizing his epic (pun intended – wait for Hot Point, below) book, The Creative Destruction of Medicine. A founder of the West Wireless Health Institute (now known as West Health), Dr. Topol is a physician and researcher at Scripps and was recently named as editor at Medscape. A new piece of Topol Trivia for me is that GQ magazine called him a rock star of science. Dr. Topol is one of the more
A health economics lesson from Jonathan Bush, at the helm of athenahealth
At HIMSS13 there are the equivalent of rock stars. Some of these are health system CIOs and health IT gurus who are driving significant and positive changes in their organizations, like Blackford Middleton, Keith Boone, Brian Ahier, and John Halamka. Others are C-level execs at health IT companies. In this latter group, many avoid the paparazzi (read: health trade reporters) and stay cocooned behind closed doors in two-story pieces of posh real estate on the exhibition floor. A few walk the floor, shake hands with folks, and take in the vibe of the event. We’ll call them open-source personalities. The
Patients globally would embrace Jetsons-style health care…but will health providers?
Patients are getting comfortable with remote health care – that is, receiving care from a health provider at a distance via, say, telehealth or via a Skype-type of set-up. Furthermore, 70% of people globally saying they would trust an automated device to provide a diagnosis that would help them determine whether or note they needed to see a doctor. Based on the findings from Cisco‘s survey summarized in the Cisco Connected Customer Experience Report – Healthcare, published March 4, 2013, just-in-time for the annual 2013 HIMSS conference, a majority patients the world over are embracing health care delivered via communications
The future of sensors in health care – passive, designed, integrated
Here’s Ann R., who is a patient in the not-too-distance-future, when passive sensors will be embedded in her everyday life. The infographic illustrates a disruption in health care for people, where data are collected on us (with our permission) that can help us improve our own self-care, and help our clinicians know more about us outside of their offices, exam rooms and institutions. In Making Sense of Sensors: How New Technologies Can Change Patient Care, my paper for the California HealthCare Foundation, I set out to organize the many types of sensors proliferating the health care landscape, and identify key
Digital health investment: greenhousing innovation and the accelerator
Traditional venture capital in health care is so 2010: welcome to The Greenhouse Effect: How Accelerators Are Seeding Digital Health Innovation, explained in a new report from California HealthCare Foundation written by Aaron Apodaca. Aaron clearly explains the growing interest in and influence of health accelerators, which grew out of the first era of the Internet (read: dot-com bust v 1.0) and the founding of the Y Combinator, an internet incubator that made relatively small investments in exchange for equity positions in start-ups. Health accelerators emerged around 2011, first with Rock Health in San Francisco, which was quickly followed by
Time is of the essence — ARRA as HIT-adoption stimulus bill
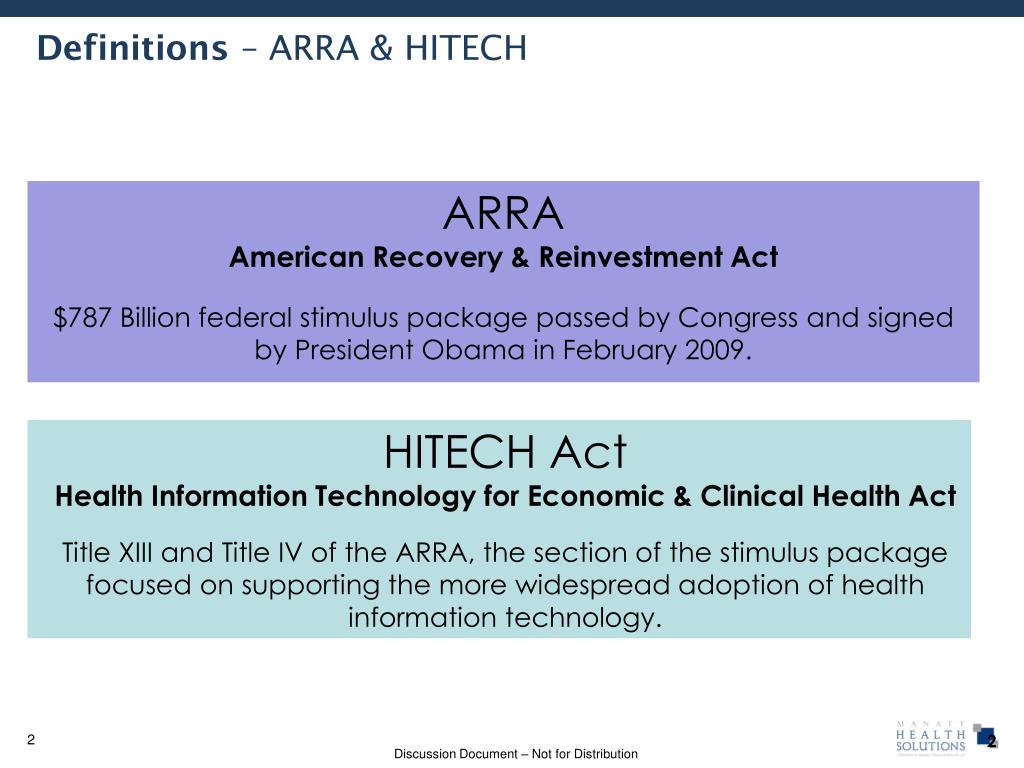
“The world changed yesterday at 1 pm Mountain time,” Steve Lieber, President of the Health Information Management Systems Society (HIMSS), told over 1,500 attendees of a webinar on February 18. These new times, Lieber said, “will require our vendor community to react a little bit differently and change business practices.” Lieber said that health information technology vendors will need to be, in his words, “more forthcoming” as well as “make absolute iron clad binding agreements.” The bottom line: time is of the essence, based the HIT details written within the 1,100 pages of
The Health Data Vault, circa 1999
Today, October 4, Microsoft unveiled its long-awaited electronic health records system, Health Vault. In a white paper called Concepts of the Health Data Vault, the author discusses the value of an individual’s “health data bitstream.” The author goes on to say that, “The value of this bitstream is based on its organization and communication within an individual’s context. This value is not necessarily reflected in specific dollars and cents savings, but rather in the individual’s health, trust in the healthcare system, and community. It has the potential to radically shift the balance of power in today’s health care system.” This





 Thank you FeedSpot for
Thank you FeedSpot for