Trust and authenticity are the enablers of health engagement
Without trust, health consumers won’t engage with organizations who want to cure them, sell to them, promote to them, help them. Here’s what I told a group of pharmaceutical marketers at The DTC Annual Conference in Washington , DC, on April 9, 2010. Let’s start with the World Health Organization’s definition of health: that is, the state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing, and not just the absence of disease. This definition is being embraced by health citizens long before the silos in the health industry – including pharma – get it. That’s an important mindset to take on as
Diagnosis: sicker people have less Internet access
While 2 in 3 American adults with no chronic health conditions go online to access health information, only 1 in 2 chronically ill people seek health information online. This irony here is that those who most need access to online information, support and tools don’t use them as much as people who are healthy. “The Internet access gap creates an online health information gap,” say Susannah Fox and Kristen Purcell of the Pew Internet & American Life Project in their landmark report, Chronic Disease and the Internet. It’s not that sicker people aren’t interested in accessing health information; it’s that
Flipping cancer the bird: can pop culture cure cancer?
70,000 young Americans between 15 and 39 years of age are diagnosed with cancer every year. This population falls in a gap between pediatric and adult cancer. Newly-diagnosed young adults often find themselves in a no-patients’-land, confronting a lack of targeted clinical trials and knowledgeable clinicians in local health markets.The National Cancer Institute says that survival rates for this group of cancer patients haven’t improved in over 30 years.That’s definitely cause to flip cancer the bird, and that’s exactly what the young actor, Zac Efron, has done.Efron is photographed with a young cancer patient, Emily Hobson, to focus on Stupid
Health is contagious: the nature of connected-ness
The book Connected was recommended by my colleague, intellectual beacon and friend, Susannah Fox of the Pew Internet & American Life Project. In the midst of late nights analyzing health reform scenarios and medical microeconomics, I’ve made the time to read this book in its entirety. It’s been a worthwhile investment. Previously, the authors of Connected, Nicholas Christakis and James Fowler, found evidence on connectedness in health in the areas of obesity, smoking cessation, binge drinking, and other lifestyle behaviors that directly impact good or bad health. This week, another team of innovative thinkers led by John Caccioppo from the
Americans like mobile health, especially for exams, wellness, and monitoring
If mobile medical services were available to Americans today, 40% would use the service in addition to seeing their doctors.23% of people would replace the doctor with mobile medical services. 1 in 3 people wouldn’t use the service at all. Welcome to the era of “m”-everything — mobile-everything, 24×7. And health is a natural partner for “m.” These stats come from a survey released by CTIA-The Wireless Association, in conjunction with The Harris Poll. The poll was conducted among American adults in September 2009. The 23% of health citizens who would use mobile health services instead of going to the
Learning about social networks and health in Omaha
There’s a groundswell driving social media in health care in America, from Silicon Valley to Boston, Miami to…Omaha? Strategy& (former Booz and Company) and the Center for Health Transformation convened a roundtable discussion in Omaha, Nebraska, in March 2009 following up a discussion the company had in 2008 with stakeholders in diabetes. In that meeting, the opportunities generated by social media in the field of diabetes were explored, with respect to improving peoples’ access to information for health and wellness, as well as how to use social media to influence policy and positive health behaviors. As I pointed out in my
Demand for health products and services is down in the recession; thinking about value and self-care in health
What is value in health care? Every year we spend more and seem to get less, John Seng, Founder of Spectrum, told attendees of a webinar on the Spectrum Health Value Study on 12th May 2009. As we consumers spend more of our own money, we’ll be looking for greater value and “health ROI” from our health spending. Measuring value across a population is confounded by the fact that what one person decides to spend on ‘health’ can be different from another’s health spending choices. In other words, our personal health “marketbaskets” for health spending vary from person to person.
Nearly 1 in 2 women delayed health care in the past year due to costs – the economic impact on a woman’s physical, emotional, and fiscal health
Nearly 1 in 2 women put off seeking health care because the cost was too high. The kinds of services delayed included visits to the doctor, medical procedures, and filling prescription medications. The fourth annual T.A.L.K. Survey was released this week by the National Women’s Health Resource Center (NWHRC), focusing on the declining economy and its impact on women and three dimensions of their health — physical, emotional, and fiscal. 40% of women say that their health has worsened in the past five years due to increasing stress and gaining weight, according to the survey. One of the most interesting
Don’t cross Baby Mama — McNeil Will Need More Than Motrin For This New Headache
It all started with a baby, a baby carrier, and Motrin. Oh, and an advertising agency who probably got their Mommy-messaging more than a little bit wrong. Twitter, the social networking software, helped fuel this uproar in a matter of hours. In what is to-date among the fastest viral campaigns in consumer health — that backfired –well over a hundred of mommy blogs and countless Twitter messages expressed emotions on a continuum from outrage to insult about a new campaign targeted to Moms who carry their babies in on-the-body carriers. The ad begins, “Wearing your baby seems to be
Moving up the health care value chain: J&J in health services
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) has acquired the online health coaching company, HealthMedia. This will move the health supply company up the health care value chain further into the provision of health services. Nine years ago, I teamed with a Big Pharma on a scenario planning exercise about consumers and health care. One of our scenarios told the future-story of the consolidation/integration of information technology, pharma/life sciences, and health services to benefit consumer health. We now meet up with this future-story, and it’s J&J’s to tell. I’ve written here in Health Populi about Walmart’s move toward pharmacy benefits management and
Trusting strangers: implications for health
Welcome to the new influence landscape, says Universal McCann (UM), the global media agency. In When Did We Start Trusting Strangers: The How the Internet Turned Us All into Influencers, UM analyzed the online behaviors of thousands of Internet users in 29 countries. UM found that today, we trust strangers as much as close friends. Furthermore, “friendship is no longer local or face to face: it’s becoming distant and virtualized,” the report asserts. Most importantly, the power of social media affords everybody with access to the Internet to be an influencer. Social media adoption in this study includes: Read blogs/weblogs
Centenarians say a long life is all about staying connected
The key to longevity isn’t about taking vitamins or consuming health care or yogurt…it’s staying connected to family, friends, and world events. That news comes to us from the third Evercare 100 @ 100 Survey which details ultra-seniors’ views on politics and the good life. Evercare surveyed in-depth 100 centenarians. Collectively, their views challenge stereotypes of the oldest Americans alive today. There are 84,000 of them, according to the U.S. Bureau of the Census. For example, 19% of centenarians use cell phones, 7% email, and 3% online date. Google is a boon to looking for old, lost friends.
Aging, economics and consumer-generated media — implications for health
Advertising Age analyzes census data on aging and diversity in America, and comes up with some interesting conclusions for consumer marketers. Here at Health Populi, we’re all-health, all-the-time, so I’m going to discuss author Peter Francese’s findings through our health lens. In addition, McKinsey published its insights into aging boomers in the report, Talkin’ ‘Bout My Generation, which I will also discuss. Francese begins with the one-two punch that marketers in the U.S. are already faced with the economic downturn coupled with consumer-generated media (e.g., blogs, online videos, e-pinions.com, ad infinitum). The third challenge to add to these two market-shapers
How social media in health helped women in itchy bras
Renenber the hair product ad for Clairol Herbal Essence shampoo that ran in the 1980s where one woman tells another, who tells another, who tells another about the merits of the shampoo? Social media behaved in just this way when women share their personal stories about allergies they developed when wearing the same style of bra. Here’s the post from December 23, 2007, from Catherine145. She says, “I recently bought a Victoria Secret padded demi bra. I am also dieting so when my top began to itch I originally associated it with the fact that everything was shrinking.” She then spoke with
Searching vs. using health information: the "just looking" mode of health search
Consumers, at least Californians, do a lot of looking for health information on the Internet — but very little health management. California HealthCare Foundation (CHCF) has taken a snapshot of Californians’ use of the Internet in health care. The profile is presented in CHCF’s report, Just Looking: Consumer Use of the Internet to Manage Care. Topline: insured, more affluent, and younger people use the Internet in health searching. The most popular care-related uses on the Internet include searching for information about conditions and drugs, finding a physician, checking ratings, and looking for claims and benefit information online.
A profile of silver surfers: don’t discount older web-searchers
There’s a growing cadre of older people online, and they’re an attractive demographic, according to Focalyst, a joint venture of the AARP and Millward Brown, a market research and branding company. The researchers found that “matures” spend 750,000,000 minutes a day on the Internet (sounds like a song from Rent–the AARP version of 525,600 Minutes). Focalyst calls the group of people age 62 and over “Matures Online.” The Insight Report: April 2008 finds that matures are just as likely to be persuaded by an Internet ad as younger consumers. Is this what Martha would consider a “good thing” or not-so-good?
The Future of Telehealth, according to Philips
While fiscal, billing and back office technologies universally proliferate home care, only 17% of agencies use some type of telehealth systems. However, 32% of agencies with over $6mm in annual revenue provide telehealth services. Thus, size matters when it comes to home health adopting telehealth technologies. These are just a couple of many important benchmarks published in the National Study on the Future of Technology and Telehealth in Home Care. Billed as the largest telehealth study in the history of home care, Philips unveiled this report in conjunction with the 13th annual American Telemedicine Association conference in Seattle. Philips partnered
Profiles of older health care consumers: living longer, longing for technology
Older Americans are healthier and more prosperous than previous generations. Furthermore, older people want to adopt technologies that will help them age well in their homes. Two new reports together provide a new look into aging in America. Older Americans 2008: Key Indicators of Well-Being is a wide-reaching data compendium which paints a current profile on aging in America through 38 measures that depict the well-being of older Americans. Measures include demographics, economics, health status, health risks and behaviors, and the cost and use of health services. The Chartbook is well worth reviewing to gain insights into this fast-growing population
Who do you trust? Edelman’s Trust Barometer says “people like me,” tech, life science, and banks — not insurance, media, or government
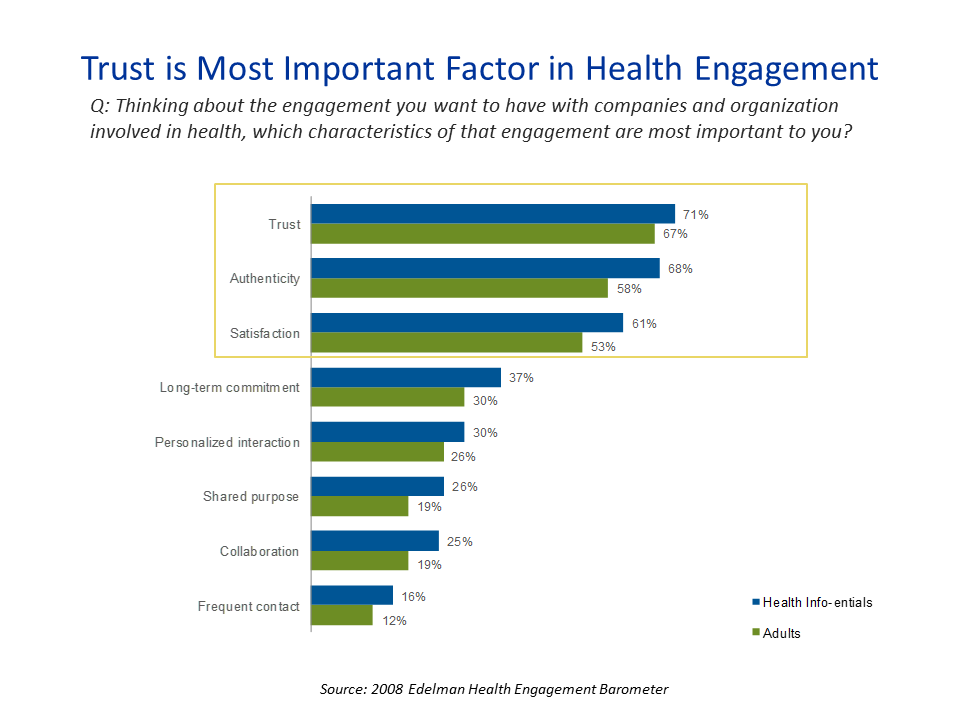
The 2008 Edelman Health Engagement Barometer is out alongside the company’s annual Trust Barometer, and more than ever, people are trusting “people like me” more than they do institutions. This is the ninth iteration of the Trust survey. The toplines of the past four years show an important change in peoples’ trust perspectives. In 2005, Edelman found that trust in ‘established institutions’ and figures of authority began shifting to peers. By 2006, “A person like me” was the most credible spokesperson for companies. That year, people trusted employees significantly more than company CEOs. Edelman defines “a person like me” as





 I was invited to be a Judge for the upcoming
I was invited to be a Judge for the upcoming  Thank you Team Roche for inviting me to brainstorm patients as health citizens, consumers, payers, and voters
Thank you Team Roche for inviting me to brainstorm patients as health citizens, consumers, payers, and voters  For the past 15 years,
For the past 15 years,